You can Download Circles Questions and Answers, Activity, Notes PDF, Kerala Syllabus 10th Standard Maths Solutions Chapter 2 help you to revise complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
SSLC Maths Chapter 2 Circles Textbook Questions and Answers
SCERT Class 10th Standard Maths Chapter 2 Circles Notes
Textbook Page No, 42
Circles Class 10 Kerala Syllabus Question 1.
Suppose we draw a circle with the bottom side of the triangles in the picture as diameter. Find out whether the top corner of each triangle is inside the circle, on the circle or outside the circle.

Answer:
Angle of the first triangle =110°
As 110° > 90° the top comer will be inside the circle
Angle of second triangle = 90°
∴ The top comer will be on the circle.
Angle of the third triangle = 70°
70° > 90°
∴ The top comer will be outside the circle
Sslc Maths Circles Questions And Answers Question 2.
For each diagonal of the quadrilateral shown, check whether the other two corners are inside, on or outside the circle with that diagonal as diameter

Answer:
The fourth angle in ABCD
= 360 – (110 + 105 + 55) = 360

Drawing diagonal AC and taking it as diameter of a circle As, ∠D = 90°
D will be on the circle. ∠B = 55° (90 > 55°)
∴ B will be outside the circle
Drawing diagonal BD and taking it as diameter of a circle.
∠A = 105°, ∠C = 110°
As both angles are greater than 90, they lie inside the circle.
Sslc Maths Chapter 2 Kerala Syllabus Question 3.
If circles are drawn with each side of a triangle of sides 5 centimetres, 12 centimetres and 13 centimetres, as diametres, then with respect to each circle, where would be the third vertex?
Answer:
As the sides are 5, 12, 13 cm and also
52 + 122 = 25 + 144 = 169 = 132
∴ ABC is a right triangle

Taking BC as diameter and drawing a circle, ∠A (<90°), A will be outside the circle.
Taking AB as diameter and drawing a circle ∠C (<90°) C will be outside the circle.
Taking AC as diameter and drawing a circle, ∠B = 90°, B will be on the circle.
Circles Class 10 Scert Solutions Kerala Syllabus Question 4.
In the picture, a circle is drawn with a line as diameter and a smaller circle with half the line as diameter. Prove that any chord of the larger circle through the point where the circles meet is bisected by the small circle.

Answer:
∠ADO = ∠APB = 90°
(angle subtended by diameter is always 90°)
⇒ OD\\PB

AO = OB (Radius of bigger circle)
(If in a triangle, the line drawn from midpoint of one side, is parallel to another side, then the line will bisect the third side)
Therefore AD = DP
(AB’s midpoint is ‘O’ and OD\\PB)
Sslc Maths Circles Questions And Answers Pdf Question 5.

Use a calculator to determine up to two decimal places, the perimeter and the area of the circle in the picture.
Answer:

Maths Chapter 2 Class 10 Kerala Syllabus Question 6.
The two circles in the picture cross each other at A and B. The points P and Q are the other ends of the diameters through A.

i. Prove that P, B, Q lie on a line.
ii. Prove that PQ is parallel to the line joining the centres of the circles and is twice as long as this line.
Answer:

i. ∆ PAB (angle subtended by semicircle)
∠PBA = 90°
∆ ABQ be a triangle on the semi¬circle of centre D.
∴ ∠ABQ = 90°
∠PBA + ∠ABQ = 180 (Linear pair)
As AP, AQ are diameters of the circle. PQ be the line drawn through B per¬pendicularly to AB. Therefore P, B, Q lies on the same line.
ii.

Sslc Maths Circles Notes Kerala Syllabus Question 7.
Prove that the two circles drawn on the two equal sides of an isosceles triangle as diameters pass through the midpoint of the third side.
Answer:

∠ADB= 90° (AABD angle subtended by semicircle)
∠CDA = 90°
∴ ∠ADB +∠CDA = 180° (linear pair)
∆ ABD ∆ ADC are right angled triangles.
In ∆ ABD
BD2 = AB2 – AD2 ( AB = AC )
= AC2 – AD2 = DC2
BD = CD
Sslc Maths Chapter 2 Circles Questions And Answers Question 8.
Prove that all four circles drawn with the sides of a rhombus as diameters pass through a common point.

Prove that this is true for any quadrilat¬eral with adjacent sides equal, as in the picture.

Answer:

ABCD is a rhombus so diameter are perpendicular bisectors.
∠AOD = 90°
O be on the circle having diameter AD.
∠AOB = 90°, therefore
O be on the circle having diameter AB.
∠BOC= 90°, therefore
O be on the circle having diameter BC
∠DOC= 90°, therefore
O be on the circle having diameter DC
O be the common point on the circle.
∠A0D = ∠AOB and
∠COD = ∠BOC and,
AD = AB,
AO be the common side.

Δ AOD, Δ AOB are equal triangles.
OD = OB
Both the circles can passed through O.
A BCD is an isosceles triangle.
Those circles having diameters CD and BC are passing through midpoint of BD.
∴ O be common for the four circles. (Diameter)
Sslc Maths Chapter 2 Circles Notes Kerala Syllabus Question 9.
A triangle is drawn by joining a point on a semicircle to the ends of the diameter. Then semicircles are drawn with the other two sides as diameter.

Prove that the sum of the areas of the blue and red crescents in the second picture is equal to the area of the triangle.
Answer:

Area of triangle = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 2r × h = rh
Area of the semicircle = \(\frac{\pi r^{2}}{2}\)
Area of the rest of the figure
![]()
The diameters of the red and blue semi-circles are the sides of the two triangles.
∴ Their areas
![]()
Area of red and blue crescents
![]()
= area of the triangle
Textbook Page No. 53
Circles Class 10 Notes Pdf Kerala Syllabus Question 1.
In all the pictures given below, O is the centre of the circle and A, B, C are points on it. Calculate all angles of Δ ABC and Δ OBC in each.

Answer:
a.

OA = OB (radii)
∴ ∠OAB = 20° ; (∠OAB = ∠OBA)
OC = OA (radii) ;
∠OAC = 30°
∠BAC = ∠OAB + ∠OAC
= 20 + 30 = 50°
∠BOC = 2x ∠BAC = 100°
OB = OC (radii)
∴ ∠OBC = ∠OCB = 40°

Angles of triangle ABC are ∠BAC = 50° ∠ABC = 60°, ∠ACB = 70°
Angles of ∆ BOC are
∠OBC = 40°, ∠OCB = 40°, ∠BOC = 100°
b.

Angles of ∆ ABC are ∠ABC = 50°, ∠BAC = 60°, ∠BCA = 70°
Angles of ∆ AOC are
∠OAC = 40°, ∠AOC = 100°, ∠OCA = 40°
c.

∠ACB = 180 – 55 = 125° ; OA = OC
∠CAO = ∠ACO = 70° ; ∠OBC = ∠BCO = 55° Angles of A OBC are
∠OBC = 55° ∠COB = 70° ∠BCO = 55°
Angles of ∆ ABC

Class 10 Maths Chapter 2 Circles Kerala Syllabus Question 2.
The numbers 1,4,8 on a clock’s face are joined to make a triangle.

Calculate the angles of this triangle.
How many equilateral triangles can we make by joining numbers on the clock’s face?
Answer:
The angle subtended by two adjacent numbers at the centre of the clock is 30°

We can make 4 equilateral triangles by joining the numbers on the clock (1. 5, 9), (2, 6, 10), (3. 7, 11), (4, 8, 12)
10th Class Maths Chapter 2 Circles Kerala Syllabus Question 3.
In each problem below, draw a circle and a chord to divide it into two parts such that the parts are as specified.
i. All angles on one part 80°.
ii. All angles on one part 110°.
iii. All angles on one part half of all angles on the other.
iv. All angles on one part, one and a half times the angles on the other.
Answer:
i. ∠AOB = 160°
Therefore all angles in the are ACB arc 80°.

ii. Draw angle as central angle 220° so angle on the small arc AB will be 110°.

iii. Draw angle as central angle 120° or 240° All angles on one part will be 120°, and other part be 60°.

iv. Draw a circle and draw central angle 144° All angles on the part APB will be 120° and All angles on the part AQB will be 108°.

Sslc Maths Chapter 2 Circles Kerala Syllabus Question 4.
A rod bent into an angle is placed with its corner at the centre of a circle and it is found that \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 }\) of the circle lies within it. If
it is placed with its corner on another circle, what part of the circle would be within it?

Answer:

Circles Class 10 Notes Kerala Syllabus Question 5.
In the picture, O is the centre of the circle and A, B, C are points on it. Prove that
∠OAC + ∠ABC = 90°

Answer:

Class 10 Maths Chapter 2 Kerala Syllabus Question 6.
Draw a triangle of circumradius 3 centimetres and two of the angles 32\(\frac { 1° }{ 2 }\) and 37\(\frac { 1° }{ 2 }\)
Answer:
Draw a circle with radius 3 cm and central angle 65°.
Half of 65° is 32\(\frac { 1° }{ 2 }\) Similarly we can draw 75°
Join the points A, B and C Halfof75°is 373\(\frac { 1° }{ 2 }\) Complete the triangle.

Circles Class 10 Notes State Syllabus Question 7.
In the picture, AB and CD are mutually perpendicular chords of the circle. Prove that the arcs APC and BQD joined together would make half the circle.

Answer:
If ∠ADC = x
∠AOC =2x
(Angle subtended on the alternate arc is half of the central angle of arc )
If ∠BAD = y
∠BOD= 2y
∠AOC + ∠BOD = 2x + 2y
= 2 (x + y) = 2 × 90 = 180°
∴ The arcs APC and BQD joined together will make half the circle.

Kerala Syllabus 10th Standard Maths Chapter 2 Question 8.
In the picture, A, B, C, D are points on a circle centred at O. The lines AC and BD are extended to meet at P. The line and BC intersect at Q. Prove that the angle which the small are AB makes at O is the sum of the angles it makes at P and Q.

Answer:

Textbook Page No. 59
Kerala Syllabus 10th Standard Maths Circles Question 1.
Calcula te the angles of the quadrilateral in the picture and also the angles between their diagonals:

Answer:
Since
∠ACD = 30°
∠ABD = 30°
(Angle in the same segment of a circle)
Since ZCBD = 45°
∠CAD = 45°
Since ZBDC = 50°
∠BAC = 50°
∠ABC + ∠ADC = 180 (cyclic quadrilateral)
∠ABC = 75°
∴ ∠ADC = 180 – 75 = 105°

∠ADB = 105 – 50 = 55°
As, ∠BAD = 95°
∠DCB = 180 – 95 = 85°
∴ ∠ACB = 85 – 30 = 55°
Circles Class 10 State Syllabus Kerala Syllabus Question 2.
Prove that any outer angle of a cyclic quadrilateral is equal to the inner angle at the opposite vertex.
Answer:

PQRS is cyclic Quadrilateral
∠PSR + ∠PQR = 180°
(sum of opposite angles)
∠PQR + ∠RQT = 180° (linear pair)
From this we get ∠PSR = ∠RQT
Maths Circles Class 10 State Syllabus Question 3.
Prove that a parallelogram which is not a rectangle is not cyclic.
Answer:
PQRS is cyclic quadrilateral.
∠P + ∠R = 180
Also in a parallelogram opposite angles will be equal.
∠P + ∠R = 180°
∠P = ∠R = 90°
This means that PQRS must be a rectangle, otherwise, it is not cyclic.

Sslc Maths Chapter 2 Notes Kerala Syllabus Question 4.
Prove that any non-isosceles trapezium is not cyclic.
Answer:

opposite angles are not supplementary.
∴ ABCD is not cyclic. Non-isosceles trapezium is not cyclic.
10th Class Maths Notes Kerala Syllabus Question 5.
In the picture, bisectors of adjacent angles of the quadrilateral ABCD intersect at P, Q, R, S.

Prove that PQRS is a cyclic quadrilateral.
Answer:

2x + 2y + 2z + 2w = 360°;
x + y + z + w = 180°
Δ DPC; ∠DPC = 180 – (w + z)
Δ ARB ; ∠ARB =180 – (x + y)
∠R + ∠P = 360 – (x + y + z + w) = 360 – 180 = 180°
In ΔBQC ZQ = m – (w + x)
In Δ ASD ∠S = 180 – (r + y)
Similarily ∠S +∠Q = 180.
PQRS is a cyclic quadrilateral.
Question 6.
i) The two circles below intersect at P, Q and lines through these points meet the circles at A, B, C, D. The lines AC and BD are not parallel. Prove that if these lines are of equal length, then ABDC is a cyclic quadrilateral.

ii) In the picture, the circle on the left and right intersect the middle circle at P, Q, R, S; the lines joining them meet the left and right circles at A, B, C, D. Prove that ABDC is a cyclic quadrilateral.

Answer:
i.

∴ ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral.

ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral.
Question 7.

In the picture, points P, Q, R are marked on the sides BC, CA, AB of AABC and the circumcircles of ΔAQR and ΔBRP are drawn. M is a point where these circles intersect.
Prove that the circumcircle of ΔCPQ also passes through M.
Answer:

Let M be a common point which three circles can passed.

Therefore the circumcircle of ACPQ also passes through M
Textbook Page No. 67
Question 1.
In the picture, chords AB and CD of the circle are extended to meet at P.

i. Prove that the angles of Δ APC and Δ PBD, formed by joining AC and BD, are the same.
ii. Prove that PA × PB = PC × PD.
iii. Prove that if PB = PD, then ABDC is an isosceles trapezium.
Answer:

i. As ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral.
If ∠BAC = x° then
∠BDC = 180 – x ∠BDP = x°
If ∠ACD = y° then ∠PBD = y°
As ∠APC is common angle.
Angles of Δ APC and Δ PBD are same

iii. If PB = PD ; AP= PC
In ABCD
ABDC is a cyclic quadrilateral, so their opposite angles are supplementary.
If AP = PC, in ∆ APC
∠A =∠C

As AB = CD
AC || BD
Adjacent angles are supplementary
∴ ABCD will be an isosceles trapezium
Question 2.
Draw a rectangle of width 5 centimetres and height 3 centimetres.
i. Draw a rectangle of the same area with width 6 centimetres.
ii. Draw a square of the same area.
Answer:
i. Draw a rectangle of length 5 cm and width 3cm.

Extend AB up to 6cm.
(AE = 6cm) Draw an arc having radius as AE and A as centre. Extend DA and mark the point F.

Extend BA towards left. Mark G as AD = AG
Draw Δ GFB.

Circum circle of Δ GFB meets AD at D.
∴ AG × AB = AF × AH.
That is area of the rectangle having length AB and width AD is equal to the area of rectangle having length AE and width AH.

ii. Draw a rectangle of length 5cm and width 3cm. Area = 5 x 3 = 15 cm2.
Therefore side of a square will be √15.

Draw a semicircle of diameter AH.
Extend BC, and mark the point F.
AB × BH = 5 × 3 = 15
AB × BH = BF2 ; BF = √5 cm
Area of BEGF = √15 × √15 = 15 cm2
Question 3.
Draw a square of area 15 square centimetres.
Answer:
Draw a rectangle of length 5cm and width 3cm. Area = 3 × 5 cm2 = 15 cm2. Side of the square is √15.
Draw a semicircle of diameter AH.
BC can touch the point F.
AB × BH = BF2 = √152 = 15 cm2.
Area of BEGF = 15 cm2.
Question 4.
Draw a square of area 5 square centimetres in three different ways. (Recall Pythagoras theorem)
Answer:
i. Draw a rectangle of length 5cm and width 1 cm.

Draw a semicircle of diameter AE. Extend BC up to F. √5 is the side of the square BGHF.
ii. Draw a right-angled triangle of perpendicular sides 2 cm and 1cm.

Hypotenuse will be y is cm. The area of the square ACDE is 5 cm2, because here we take the hypotenuse as sides of the square.
iii. Draw a right-angled triangle of hypotenuse 3 cm and one side 2cm.
Third side = \(\sqrt{3^{2}-2^{2}}=\sqrt{5} \mathrm{cm}\)
Draw a square having side BC, then area of the square BEDC will be 5cm2

Question 5.
In the picture, a line through the centre of a circle cuts a chord into two parts:

What is the radius of the circle?
Answer:

The intersection may be with in the circle.
Chords AB & CD intersect at P i. e.,
AP × PB = CP × PD
(The intersection will be inside the circle)
AP × PB = CP × PD
4 × 6 = CP × (OP + OD)
24 = CP × (OP + OC)
24 = CP × (OP + OP + CP)
24 = CP × (5 + 5 + CP)
24 = CP × (10 + CP)
CP =2
Radius = CP + OP = 2 + 5 = 7cm
Question 6.
In the picture, a line through the centre of a circle meets a chord of the circle:

What are the lengths of the two pieces of the chord?
Answer:


CP= 13 – PB
Therefore equation (1)
(13 – PB)PB = 40
PB = 5, 8
If PB = 5cm then PC = 8cm
If PB = 8cm then PC = 5cm
In figure PB > PC
PB = 8 cm, PC = 5 cm
Circles Orukkam Questions & Answers
Worksheet 1
Question 1.
In triangle ABC, AB = 8cm, BC = 6cm , AC = 10cm.
1. What kind of triangle is this?
2. What is the position of B based on the circle with AC as the diameter? Why?
3. What is the position of A based on the circle with BC as the diameter? Why?
4. What is the position of the point C based on the circle with diameter AB?
Answer:
In Δ ABC
AB2 + BC2 = 82 + 62 = 64 + 36 = 100 = AC2
Δ ABC is a right angled triangle.
If we draw a circle taken in a AC as diameter, ∠B = 90°, Therefore the point B on the circle.
Δ ABC is a right-angled triangle.
If we draw a circle taking BC as diameter, ∠A < 90°, Therefore the position of point A will be outside the circle.
If we draw a circle taking AB as diameter, ∠C < 90°, Therefore the position of point C will be outside the circle.
Question 2.
Three vertices of a parallelogram are on a circle and the fourth vertex is at the center. Find the angles of the parallelogram.

Mark a point P on the top of the figure on the circle, join AP and CP. If angle AP C = x then write? AOC
Write ABC?
Write ∠ABC + ∠APC ?
What is APC?
Find the angles
Answer:

The angles of a parallelogram are 60, 120, 60 and 120.
Question 3.
In triangle ABC ,AB = AC, angle BAC = 30, BC = 5cm Find the radius of ABC
Draw the figure
Mark the center, BO and CO
Find the measure of angle BOC
Write the angles of triangle OBC
What kind of angle is triangle OBC
Write the radius of the circumcircle
Answer:

∠OBC= 75 – 15 = 60 = OCB (∵OB = OC)
Angle of Δ OBC are: 60, 60, 60
ΔOBC is an equilateral triangle.
Radius of circum circle of Δ OBC = OB = OC = BC = 5 cm.
Question 4.
P QRS is cyclic.
∠P = 3x, ∠Q = y, ∠R = x, ∠ = 5 v
Find the angles
Draw circle , mark P, Q, R, S on it, complete PQRS Enter the given angles.
What is 3x + x? Find x
What is y + 5y? Find y
Find the angles
Answer:

3x + x = 180° (Sum of the opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral is 180″)
=> 4x = 180° => 4x = 45°
y + 5y = 180 (Sum of the opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral is 180°)

Question 5.
In the figure ABC D is a trapezium. If the vertices are on a circle, prove that it is an isosceles trapezium draw figure
What is ∠A + ∠C?

What is ∠B + ∠C?
Write the relation between A and B. Write the conclusion.
Answer:

∠A + ∠C = 180° (Sum of the opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral is 180°)
∠B + ∠C = 180° (AB || CD)
(Sum of the alternate angles of a cyclic quadrilateral is 180″)
∠A + ∠C = ∠B + ∠C
∴ ∠A = ∠B
∴ ABC’D is an isoceles trapezium
Question 6.
In ABC AB = AC . P is the midpoint of AB and Q is the midpoint of AC. Prove that BPQC is cyclic?
Draw figure. Mark PQ and complete BP QC?
Is PQ parallel to BC?
Note that ∠B = ∠C?
What is ∠C + ∠Q?
What is ∠B + ∠Q?
Write conclusion.
Answer:

PQ || BC
(The line joining midpoints of two sides of a circle will be parallel to the third side).
∠B = ∠C (1)
(∵ AB = AC are given )
∠C + ∠Q = 180° (2)
(∵ PQ || BC, QC is the bisector, so the sum of alternate angles are 180°)
∠B + ∠Q = 180° .
From (1) and (2) we conclude that BPQC is an cyclic trapezium
Worksheet 2
Question 7.
Prove that ABCD given in the figure is cyclic

Draw figure and mark PQ
If ∠BAP =xthen
what is ∠BQP?
Find ∠PQD
Find ∠PDC? Why?
What is ∠A + ∠C?
Answer:
i. Quadrilateral ABPQ is cyclic
If ∠A = x, then ∠BQP = 1 80 – x
If ∠B = y, then ∠APQ = 180 – y
Quadrilateral PQCD is cyclic, SO
∠QCD = 180 – x (∠DPQ = x )
∠PDC = 180 – x (∠PQC = y)
∴ ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral.
Worksheet 3
Question 8.
In the figure AB, C Dare extended and intersect at P. If AB = 5, BP = 3, P D = 2 then find CD? Draw the figure.

Write the relation between PA, PB, PC, PD
Find C D
Answer:
PA x PB = PCxPD
If CD = x, then
⇒ 8 × 3 = (2 + x)2 ⇒ 24 = 4 + 2x
⇒ 2x = 20 ⇒ x = \(\frac { 20 }{ 2 }\) = 10
∴ CD= 10
Question 9.
In the figure AB is the diameter and CD is parallel to the diameter. AB = 8cm,BD = 2cm, find CD

Answer:
If we draw a perpendicular DP to AB from D. Then PAxPB = PD2.
Here PB = x, then PA = 8 – x.

x(8 – x) = PD2, 22 = x2 + PD2
x(8 – x) = 4 – x2, 8x – x2 = 4 – x2
8x = 4, x = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
Similarly, let us draw a perpendicular CQ to AB from C
AQ = ,PQ = 8– \(\left(\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{2}\right)\) = 7
CD = 7cm
Question 10.
Draw a rectangle of length 6cm and width 4cm. Draw another rectangle whose area equal to area of the first rectangle and one of the sides is 8cm.
Ans: Draw ABCD as in the given measurement. Mark E by extending AB 2cm more. AE = 8 will be 8cm. WithAas centre and AE radius draw an arc. This arc cut DA produced at F. Extend BA such that AD = AG and mark G. Draw triangle GF B and construct a circumcircle. The circle meets AD at H . Complete the rectangle AHIE

Worksheet 4
Question 11.
Draw an equilateral triangle of height 3cm. What is the length of a side?

Write the principle of construction. Students are advised to construct as in the steps given below.
Answer:
Draw a circle of radius 2cm and mark a diameter AB which is 4cm. Mark a point P from one end A is 3 cm apart on the diameter.
Draw a chord C D perpendicular to AB. Complete triangle C AD.
Using PA x PB = PD2, PD= √3.
Now we get AD = AC = C D = 2√3
Height AP = 3cm.
Worksheet 5
Question 12.
In the figure, PA is a tangent and O is the centre of the circle. P A = 17, ∠OPA = 30° then calculate the radius of the circle and distance from centre to the point P Triangle OAP with 30°, 60°, 90° is right triangle. Using the property of this special right triangle find the radius and the distance.

Answer:
Δ OAP is a right-angled triangle having sides 30°, 60°and 90°.
Length of side which is opposite to the angle 90°, is twice the side which is opposite to the angle 30°.
Length of side which is opposite to the
angle 60°, is √3 times of the side which is opposite to the angle 30°
That is radius of the circle , OA = \(\frac { 17 }{ √3 }\)
Distance from centre to the point P
![]()
Worksheet 7
Question 13.
Draw a circle and construct 30°, 150° angles on it.
Answer:

Question 14.
Draw a circle and construct \(22 \frac{1}{2}^{0}\) on it.
Answer:

Question 15.
In triangle ABC the radius of the circumcircle is 6 cm, ∠A = 70°, ∠B = 80°. Construct the triangle
Answer:

Question 16.
Draw a rectangle of length 7cm, and width 5cm and construct a square whose area is same as the area of this rectangle.
Answer:
Draw a rectangle of length 7cm, and width 5cm. Area = 7 × 5 = 35 cm2.
Therefore length of one side of the square is √35.

Draw a semicircle taking AH as diameter Extend BC, and mark a point F.
AB × BH = 7× 5 = 35
AB × BH = BF2 ;
BF = √35cm
Area of BEGF= √35 × √35 = 35 cm2
Question 17.
Draw a rectangle of one side 5cm, width 7cm. Construct another rectangle whose one side is 8cm and area equal to the area of the first rectangle.
Answer:
Draw a rectangle of length 7cm and width 5cm.

Extend AB up to 8 cm (AE = 8cm) Draw an arc taking A as centre and AE as radius. Extend DA and mark the point F.

Elongate BA towards left, and mark G such that AD = AG.
Draw Δ GFB

Circumcircle of A GFB will meet side AD on H.
AG × AB = AF × AH.
That is area of the rectangle having length AB and width AD is equal to the area of rectangle having length AE and width AH.

Question 18.
Draw a square of side 5cm and construct a rectangle having one side 7cm and area equal to area of the square.
Answer:
Draw a square of side 5cm.

Extend AB to 7 cm
(AE = 7cm) Draw an arc taking A as centre and AE a radius. Extend DA and mark the point F.

Elongate BA towards left, and mark G such that AD = AG.
Draw Δ GFB.

Circumcircle of A GFB will meet side AD on H.
AG × AB = AF × AH.
That is area of the rectangle having length AB and width AD is equal to the area of rectangle having length AE a width AH.

Question 19.
What is the position of the vertex of an equilateral triangle with opposite side as the diameter?
Answer:

Angles of an equilateral triangle is 60° each. Position of the vertex of triangle with opposite side as the diameter is outside of the circle, because the angle is less than 90°.
Circles SCERT Questions & Answers
Question 20.
In the figure “ ABC is a right triangle
a. If a circle is drawn with AC as diameter find the position of B.
b. If a circle is drawn with BC as diameter, find the position of A. [ Score: 3 Time: 5 minutes]

Answer:
a. On the circle (1)
∠B = 90°
b. Outside the circle (1)
Position of the vertex of an triangle with opposite side as the diameter is outside the circle, because. ∠A <9o°.
Question 21.
A circle is drawn with AB as diameter. Find the positions of the points C, D, E related to the circle.

[ Score: 3 Time: 5 minute]
Answer:
C inside the circle (1)
∠C > 90°.
D on the circle (1)
∠D = 90°.
E outside the circle (i)
∠E <90°.
Question 22.
In Δ ABC and Δ PQR, BC = QR, ∠ A = ∠P, ∠Q = 90°, QR = 5 cm, PQ = 12 cm.

Find the diameter of the circumcircle of Δ ABC. [ Score: 4 Time: 6 minute]
Answer:
QR = BC (1)
∠A = ∠P (1)
PR Diameter of the circumcircle of Δ ABC (1)
Diameter = PR= \(\sqrt{12^{2}+5^{2}}=\sqrt{169}=13 \mathrm{cm}\) .(1)
Question 23.
PQ and RS are two mutually prependicular chords of a circle. < QPR=50° find< PQS. [ Score: 3, Time: 6 minute]
Answer:
∠PRS = 90 – 50 = 40° (1)
∠PQS = 40° (1)

Question 24.
O is the centre of the circle. If ∠BOC = 130° and ∠AOB = 110°. What is ∠AOC?
Find all angles of Δ ABC
 [ Score: 3, Time: 3 minute]
[ Score: 3, Time: 3 minute]
Answer:

Question 25.
Find all angles of the hexagon ABCDEF
 [ Score: 4 Time:5 minute]
[ Score: 4 Time:5 minute]
Answer:
∠ EFD = ∠EAD = 30°
∠ FE A = ∠FDA = 40°
∠FDE = ∠FAE = 35° (1)
∠BAC= ∠BDC = 45°
∠ABD= ∠ACD = 62°
∠ACB = ∠ADB= 35° (1)
∠A = 1480, ∠B = 100°
∠C = 97° ∠D= 155° (1)
∠E= 115° ∠F= 105° (1)
Question 26.
O is the centre of the circle and AB is a chord. AC is the bisector of ∠OAB. ∠OAB = 56°.
a. Prove that OC and AB are parallel,
b. Find ∠ABC and ∠OBE.

Answer:

Question 27.
O is the centre of the circle. AD and BC are perpendicular to XY. CB cuts the circle at E. Prove that –CE = AD.

Answer:
∠AEB = 90° (Angle in a semi circle) ( 1)
∠AEC=90°
∴ AECD is a rectangle
∴ AD = CE (2)
Question 28.
ABCD is a parallelogram. A, B, E, F are the points on a circle. ∠DEF = 80° Find out the angles of the quadrilateral AEFB.
 [ Score: 4, Time: 4 minute]
[ Score: 4, Time: 4 minute]
Answer:
∠AEF = 180 – 80 = 100° (1)
∠ABF = 180 – 100 = 80° (1)
∠A = 180 – 80 = 100° (1)
∠EFB = 180 – 100 = 80° (1)
Question 29.

O is the centre of the circle. ? ∠OCA = x °.
a. Find ∠OAC
b. Prove that ∠OCA + ∠ABC = 90°
c. Prove that ∠ADC – ∠OCA = 90° [Score: 4, Time: 4 minute]
Answer:

Circles Exam Oriented Questions & Answers
Short Answer Type Questions (Score 2)
Question 30.
In the figure AB is the diameter. PC is perpendicular to AB. PC = 6cm, PB = 3cm. Find the radius of the semi-circle.

Answer:
AP × PB = PC2
AP × 3 = 62
AP = 36/3 = 12 .
AB = 12 + 3 = 15
ie Radius = 15/2 = 7.5 cm
Question 31.
In Δ PQR, ZP = 60°, ∠R = 30° find whether the vertex Q on the circle with PR as diameter.
Answer:
∠P + ∠R = 60 + 30 = 90°.
∴ ∠Q = 180 – 90 = 90°.
So point Q on the circle.
Question 32.
In Δ ABC, ∠A = 60°, ∠B = 70°. Find whether the vertex C is inside or outside the circle with AB as diameter.
Answer:
The vertex C is outside the circle Since ∠C = 180 – (60 + 70) = 50° ∠90°
Question 33.
In the diagram, the central angle of arc ABC is 100° and ∠OAD is 30°. Find ∠OCD.
Answer:

∠D = 50°
As ∠OAD
is an isosceles triangle.
∠ODA = 30°
∠ODC = 20°
∴∠OCD = 20°
Question 34.
In the figure, find ∠PQB, O is the centre.

Answer:
![]()
Short Answer Type Questions (Score 3)
Question 35.
The central angle of arc ABC is 60°, then find out the following,
i) ∠D
ii) Central angle of arc AEC,
iii) ∠B

Answer:
i. ∠D = 30°
ii. Then central angle of arc AEC = 300°.
iii. ∠B = 150°
Question 36.
Show that the arcs APC, BQD when joined make a semicircle?

Answer:
∠ADC is the half of the central angle of arc APC
The central angle of are APC = 2 ∠ADC
The central angle of arc BQD = 2 ∠DAB
In triangle AOD, CD ⊥ AB, ∠AOD = 90°,
∠DAO + ∠ADO = 180 – 90° =90°,
ie, ∠DAB + ∠ADC = 90°
2( ∠DAB + ∠ADC ) = 90° × 2 = 180°
Question 37.
The central angle of the complementary arc of a circle is 40° more than 3 times the central angle of the arc. Find out the central angles of each arc?

Answer:
x + 3x + 40 = 360
4x + 40 = 360
4x = 360 – 40 = 320
x = \(\frac { 320 }{ 4 }\) = 80
∴ central angle of arc
ABC = 80
central angle of arc ADC = 360 – 80 = 280°
Question 38.
ABCD in the diagram is a rectangle. Then find out the area of the circle.

Answer:
ABCD is a rectangle ∠B = ∠D = 90°
AC in the diameter of the circle
AC = \(\sqrt{8^{2}+6^{2}}=\sqrt{64+36}=\sqrt{100}=10\)
∴ radius = 5cm
∴ Area of the circle = πr² = π × 5² = 25πcm²
Question 39.
In the figure, AD = 16cm, BD = 6cm, CD = 2cm. Find the length EF.

Answer:

Question 40.
In the given figure, O is the centre of the circle. If ∠OAP = 35° and ∠OBP = 40°, find the value of ∠x.

Answer:
Join OP
Since OA = OP and
∠APO = ∠OAP=35°
Similarly, OB = OP and ∠OPB = ∠OBP = 40°
∠APB = 35°+ 40° = 75°
∠AOB = 2 × 750 = 150°
Long Answer Type Questions (Score 4)
Question 41.
In the figure find ∠APB,∠ABQ ; where O is the centre of the circle ∠OAP = 32° and ∠OBP = 47° .

Answer:
JoinOP.
In OAP, OA = OP = Radius
∠OAP = ∠OPA = 32°
In OPR, OB = OP = radius
∠OBP = ∠OPB =47°
∠APB = 32°+ 47°= 79°
∠AQB = 180° – 79°= 10°
Question 42.
Draw a line of √7 cm.
Answer:

Question 43.
Ois the centre of the circle as shown in the figure.
Find ∠CBD.

Answer:

Takeapoint E on the circle, join AE and CE.
∠AEC= \(\frac { 100 }{ 2 }\) = 50°
∠AEC + ∠ABC = 180° (Opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilaterals)
∠ABC = 130°
∠ABC + ∠CBD = 180° (linearpair)
130°+ ∠CBD = 180°
∠CBD = 50°
Long Answer Type Questions (Score 5)
Question 44.
In the figure O is the centre of the circle. Central angle of arc AXB is 60°, arc CYD is 80°. Then find all the angles of ΔAPD.

Answer:
Central angle of arc AXB = 60°
i.e., ∠AOB = 60°
i.e., ∠ADP = 30°
Central angle of arc CYD = 80°
i.e., ∠COD = 80°
i e., ∠DPA = 40°
i e., ∠APD = 180° – (30 + 40) = 110°
Angles of = 30°, 40°, 110°
Question 45.
‘O’ is the centre of the circle ∠D = 80°, find the following measurements.

a. ∠C
b. ∠ABC
c. ∠BAC
d. ∠F
Answer:
∠D = 80°
a. ∠C = 80° (∠D and ∠C are angled on a same arc So, both are equal)
b. ∠ABC = 90°
(AC is diameter, Angle of a hemisphere is right)
c. ∠BAC = 180 – (80 + 90)
= 180 – 170 = 100
d. ∠F= 180 – 80 = 100° (Opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral are equal)
Circles Memory Map

Angle in a semicircle is right:
The angle made by any arc of a circle on the alternate arc is half the angle made at the centre.


All angles in an arc is equal:

If AB, CD are two chords, then
PA × PB = PC × PD
The area of the rectangle formed of parts into which a diameter of a circle is cut by a perpendicular chord is equal to the area of the square formed by half the chord.
PA × PB = PC2

































































































































































































































































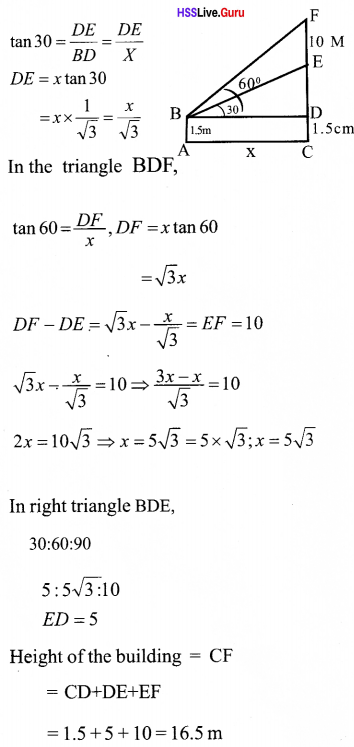

 AB = tower
AB = tower





























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































 .
.







































































































































































