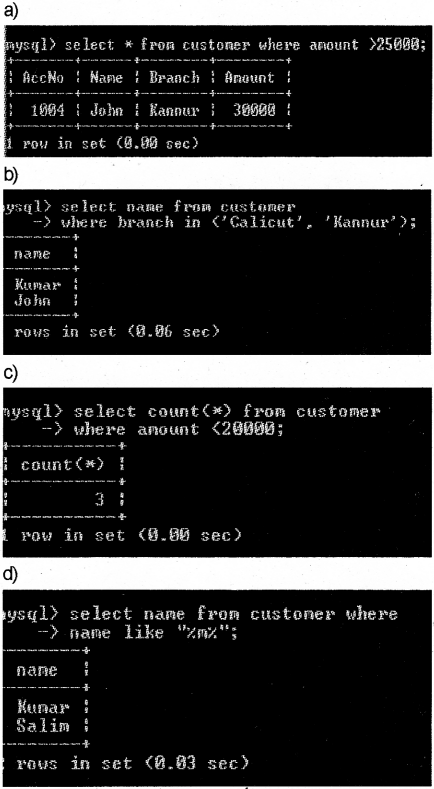
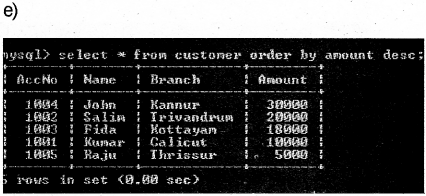
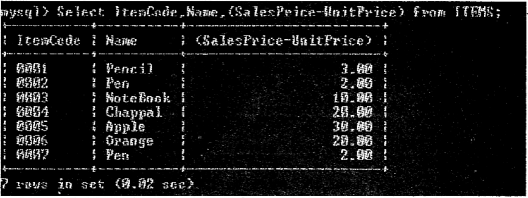
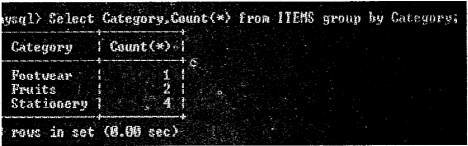
Kerala State Board New Syllabus Plus Two Business Studies Chapter Wise Previous Questions and Answers Chapter 5 Organising.
Kerala Plus Two Business Studies Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 5 Organising
Plus Two Business Studies Organising 1 Mark Important Questions
Question 1.
The technical term which denotes the number of subordinates that a superior can effectively supervise.(FEBRUARY-2009)
Answer:
Span of control
Question 2.
To satisfy social and cultural needs and to fulfill common interest, people organise themselves. What is the technical term forthis type of organisation? (FEBRUARY-2009)
Answer:
Informal organization
Question 3.
KSR Limited is a transport service company with its head office at Calicut. It has also operations and office in Thrissur, Kochi and Trivandrum.
Name the form of organisational structure suitable to this company. (MAY-2009)
Answer:
Divisional organisation
Question 4.
Anand Industries produce different types of products namely, Mobile phones, Television etc. and they have separate production managers and marketing managers for each line of products. Name the organisation structure that prevails in the firm. (MARCH-2010)
Answer:
Divisional organisation
Question 5.
Mr.Rajagopal is a foreman in a spinning mill and there are 25 employees working under him. Due to the increased number of subordinates he cannot control them effectively and hence the company could not achieve the target. Identify the element or organizational structure violated here. (MAY-2010)
Answer:
Span of control
Question 6.
Mr. Sreekumar is the leader of a marketing item. There are 25 salesmen under him. Due to the increased number of subordinates he cannot supervise them efficiently and hence the company could not achieve the target. Name the element of organisational strucutre violated here. (MAY-2011)
Answer:
Span of control
Question 7.
Identify it:
It is the framework within which an organisation functions.(MARCH-2012)
Answer:
Organisational structure
Question 8.
In which organisation, authority and responsibility relationships are not defined? (MAY-2012)
Answer:
Informal organization
Question 9.
Name the management principle which refers to concentration of authority at one place. (MAY-2013)
Answer:
Centralisation
Question 10.
Which among the following is true for formal organisation? (MAY-2013)
a) It is not clear
b) To satisfy the members
c) Importance to persons and feelings
d) To fulfill the firm’s goals.
Answer:
To fulfill the firm’s goal
Question 11.
Span of control refers to (MARCH-2014)
a) Number of managers.
b) Period of appointment of manager.
c) Number of subordinates under a Manager.
d) None of these.
Answer:
Number of subordinates under a manager.
Question 12.
In connection with Christmas celebration on the employees of National Bank formed a small group, who organized a feast and other entertainments. Name the type of organization referred here. (MARCH-2015)
Answer:
Informal organisation
Question 13.
From the following choose one which is not a part in the process of organising : (MARCH-2015)
a) Division of work
b) Grouping of jobs
c) Co-ordination of activities
d) Scalar chain
Answer:
Scalar chain
Plus Two Business Studies Organising 2 Marks Important Questions
Question 1.
Name any two elements of delegation. (FEBRUARY-2009)
Answer:
1) Identifying and grouping the work to be performed.
2) Defining and delegating authority and . responsibility.
3) and establising relationships for the purpose of accomplishing objectives.
Question 2.
In a manufacturing firm, the Production Manager entrusted a part of his work to the foreman in the factoty. Examine two possible benefitsto be gained from this forthis Foreman. (FEBRUARY-2010)
Answer:
a) Delegation of authority
b) It helps the foreman to take quick decision. It helps to develop creative skill and motivate the subordinate.
Question 3.
Rearrange the following as it takes place in the process of organising: (MARCH-2010)
a) establishing authority relationship
b) division of work
c) co-ordination of activities
d) departmentation
Answer:
Division of work
b) Departmentation
c) Establishing authority relationship
d) Co-ordination of activities
Question 4.
The following are different steps involved in the process of Organising. (MARCH-2011)
i) Grouping of similar jobs.
ii) Division of work.
iii) Co-ordination of activities.
iv) Creation of authority relationship Which of the following sequence js correct?
a) (i), (ii), (iv) & (iii)
b) (ii), (i), (iv) & (iii)
Answer:
i) Division of work
ii) Grouping of similar jobs
iii) Creation of authority relationship
iv) Co-ordination of activities
Question 5.
The aim of organizing is to enable people to work togetherfora common purpose. Explain. (MARCH-2012)
Answer:
Specialisation: Since the activities are divided into convenient jobs, and are assigned to a particular employee, it leads to specialisation, more productivity and efficiency.
Plus Two Business Studies Organising 3 Marks Important Questions
Question 1.
“Delegation of authority leads to reduction in the work load of superiors” In the light of this statement, com-ment briefly on the importance of delegation of authority. (MARCH-2009)
Answer:
1) Reduces the work load of managers : The managers are able to function more efficiently as they get more time to concentrate on important matters.
2) Employee development: Delegation empowers the employees by providing them the chance to use their skills, gain experience and develop themselves for higher positions.
3) Motivation of employees : Responsibility for work builds the self-esteem of an employee and improves his confidence. He feels encouraged and tries to improve his performance.
Question 2.
Match the following : (MAY-2009)

Answer:

Question 3.
In a classroom discussion Saleem, a Plus Two Commerce student, argues that delegation and decentralisation are one and same. (MAY-2009)
a) Do you agree with his argument?
b) Give any two points to justify your answer.
Answer:
a) No. Delegation and decentralisation are different.
b) The differences between Delegation of authority and Decentralization are :

Question 4.
Describe the importance of transferring decision making authority to the lowest levels. (MAY-2012)
Answer:
Importance of Decentralisation
1) Decentralisation helps to promote confidence amongst the subordinates.
2) It is a means of trained manpower
3) It helps in quick decision making.
4) It reduces the burden of top executives.
5) It helps to increase productivity and more returns.
6) It helps in maintaining effective control
Question 5.
Smt. Seema is a Principal of a Higher Secondary School. She decides to give some of her charges to the Vice-Principal Smt. Beena. Which function of management is used here? Explain. (MARCH-2013)
Answer:
Delegation of Authority : Delegation means the granting of authority to subordinates to operate within the prescribed limits. It enables the manager to distribute his workload to others so that he can concentrate on important matters.
Elements of Delegation
1) Authority : Authority refers to the right of an individual to command his subordinates and to take action within the scope of his position. Authority flows from top to bottom. Authority determines the superior subordinate relationship in an organisation.
2) Responsibility: Responsibility is the obligation of a subordinate to properly perform the assigned duty. Responsibility flows upwards, i.e., a subordinate will always be responsible to his superior.
3) Accountability : Accountability implies being answerable for the final outcome, i.e., subordinate will be accountable to a superior for satisfactory performance of work.
Question 6.
ABC Ltd. is manufacturing and distributing plastic home appliances.(MARCH-2014)
Draw a diagram and explain the functional organizational structure of AB Ltd.
Answer:
Functional Organisation.

Question 7.
Delegation of authority leads to inefficient superiors. (MARCH-2014)
a) Do you agree with this statement?
b) Justify your answer.
Answer:
No
b) Importance of Delegation of Authority
1) Reduces the work load of managers : The managers are able to function more efficiently as they get more time to concentrate on important matters.
2) Employee development: Delegation empowers the employees by providing them the chance to use their skills,’gain experience and develop themselves for higher positions.
3) Motivation of employees : Responsibility for work builds the self-esteem of an employee and improves his confidence. He feels encouraged and tries to improvers performance.
4) Facilitation of.growth : Delegation helps in the expansion of an organisation by providing a ready workforce to take up leading positions in new ventures.
5) Superior-subordinate relations: Delegation of authority establishes superior subordinate relationships, which are the basis of hierarchy of management.
6) Better co-ordination: The elements of delegation – authority, responsibility and accountability help to avoid overlapping of duties and duplication of effort.
Plus Two Business Studies Organising 4 Marks Important Questions
Question 1.
Delegation is the administrative process of getting things done through others and sharing authority with them. List out the importance and steps in the process of delegation. (FEBRUARY-2010)
Answer:
Importance of Delegation of Authority
1) Reduces the work load of managers : The managers are able to function more efficiently as they get more time to concentrate on important matters.
2) Employee development: Delegation empowers the employees by providing them the chance to use their skills,’gain experience and develop themselves for higher positions.
3) Motivation of employees : Responsibility for work builds the self-esteem of an employee and improves his confidence. He feels encouraged and tries to improvers performance.
4) Facilitation of growth : Delegation helps in the expansion of an organisation by providing a ready workforce to take up leading positions in new ventures.
5) Superior-subordinate relations: Delegation of authority establishes superior subordinate relationships, which are the basis of hierarchy of management.
6) Better co-ordination: The elements of delegation – authority, responsibility and accountability help to avoid overlapping of duties and duplication of effort.
Question 2.
ABC Ltd., a large size organization has five majorde- partments, viz., Production Department, Purchase Department, Personnel Department, Finance Department & Marketing Department. Which organizational structure is suitable to the company? Draw a chart showing the organizational structure of the company. (MARCH-2011)
Answer:
Functional Organisation.

Question 3.
‘Delegation and Decentralisation are one and same.’ Do you agree with this statement? Give any 4 differences. (MARCH-2013)
Answer:

Plus Two Business Studies Organising 5 Marks Important Questions
Question 1.
Hashik studying in your class has opined that there is no difference between formal and informal organisation. Do you agree? Justify your answer. (MARCH-2010)
Answer:
a) No
b)

Question 2.
Darsana Books Ltd. a leading book sellers of the State organized a book fair at Kottayam as a sales promotion programme under the control and supervision of Mr.Rajesh, the Sales Manager. On the book fairground the employees of the firm arranged a dance programme of a famous film star to collect funds for the rehabilitation of blind children of the locality. Mr. Devargjan, an employee of the firm, voluntarily acted as teh convener of the dance programme. (MAY-2010)
a) Do you find any structural difference in organising these two programmes?
b) Classify the organization of the conduct of books fair and conduct of the dance programme on the basis of their formation.
c) State any three demerits of the organization formed forthe dance programme.
Answer:
a) Yes.
b) Formal & Informal Organisation.
c) 1) It spreads rumours.
2) If informal organisation opposes the policies and changes of management, then it becomes very difficult to implement them in organisation.
3) Informal organizations lead to conflicts among employees.
Question 3.
What is ‘Delegation of Authority’ ? Explain its importance. (MARCH-2011)
Answer:
Delegation of Authority : Delegation means the granting of authority to subordinates to operate within the prescribed limits. It enables the manager to dis-tribute his workload to others so that he can concentrate on important matters.
Importance of Delegation of Authority
1) Reduces the work load of managers : The managers are able to function more efficiently as they get more time to concentrate on important matters.
2) Employee development: Delegation empowers the employees by providing them the chance to use their skills,’gain experience and develop themselves for higher positions.
3) Motivation of employees : Responsibility for work builds the self-esteem of an employee and improves his confidence. He feels encouraged and tries to improvers performance.
4) Facilitation of.growth : Delegation helps in the expansion of an organisation by providing a ready workforce to take up leading positions in new ventures.
5) Superior-subordinate relations: Delegation of authority establishes superior subordinate relationships, which are the basis of hierarchy of management.
6) Better co-ordination: The elements of delegation – authority, responsibility and accountability help to avoid overlapping of duties and duplication of effort.
Question 4.
Bhoomi daily, very often handed over some of his duties to Mr. Vijayan, the Assistant Circulation Manager. This will provide Gopalakrishnan more time to concentrate on the circulation target of the firm. In this regard. (MAY-2011)
Answer:
a) Name the element of organization applied by Gopalakrishnan.
b) State the steps to be fallowed by Mr.Gopalakrishnan before handing over the duties.
c) Do you think that the policy of decentralization can be adopted as an alternative to the above referred concept?
a) Delegation of authority
b) Elements of Delegation
1) Authority : Authority refers to the right of an individual to command his subordinates and to take action within the scope of his position. Authority flows from top to bottom. Authority determines the superior subordinate relationship in an organisation.
2) Responsibility: Responsibility is the obligation of a subordinate to properly perform the assigned duty. Responsibility flows upwards, i.e., a subordinate will always be responsible to his superior.
3) Accountability : Accountability implies being answerable for the final outcome, i.e., subordinate will be accountable to a superior for satisfactory performance of work.
c) No. Decentralisation refers to a systematic dispersal of authority to the lower levels of the orga-nization. it takes place as per the organization structure. It cannot be adopted as an alternative to delegation.
Decentralisation : Decentralisation refers to a systematic dispersal of authority to the lower lev-els of the organisation. Here decision making authority is shared with lower levels in the organisation.
Question 5.
Differentiate between formal organisation and infor-mal organisation. (MARCH-2012)
Answer:

Question 6.
Thomas, one of your friends, has decided to start a business at Kollam. He requested you to assist him in framing a suitable organisation structure. Describe the elements you should keep in mind while assisting Thomas. (MAY-2012)
Answer:
Step in the Process of Organising
1) Division of Work: The first step in the process of organising involves identifying and dividing the work that has to be done. Division of work leads to specialisation!
2) Departmentation : The second step is to group similar or related jobs into larger units, called departments. The grouping of activities is known as departmentation.
3) Assignment of duties : The next step is to allocate the work to various employees according to their ability and competencies.
4) Establishing authority – responsibility relationship: The last step is creation of authority – responsibility relationship among the job positions. It helps in the smooth functioning of the organisation.
Question 7.
General Electronics Ltd. manufacturers of electronic goods organised an exhibition of its products for sales promotion under the control of Mr.Mohan, the Sales Manager, on the exhibition ground, the employees of the company arranged a musical concert to collect funds for the rehabilitation of handicapped children of the locality. Mr. Suresh one of the employees voluntarily act as the convenor of the musical concert.
a) Do you find any structural difference in organising these two programmes. (MAY-2013)
b) Classify the organisation of the conduct of exhibition and musical concert on the basis of their formation.
c) State four demerits of informal organisation.
Answer:
a) Yes
b) Formal and informal organization.
c) i) It is not stable.
ii) No authority responsibility relationships.
iii) No formal rules exist.
iv) Cannot be presented in organization charts. No official line of communication.
Question 8.
Mr. Radhakrishnan, the Branch Manager of a nationalized bank often share some of his work to his immediate subordinate Mr. Rajendran, the Assistant Manager. This helps Mr. Radhakrishnan to spend more time to mobilize their targeted deposit. (MARCH-2015)
a) Name the element of organization applied by Mr. Radhakrishnan.
b) State the various steps to be followed in the process involved in it.
Answer:
Delegation of authority
b) Elements of Delegation
1) Authority : Authority refers to the right of an individual to command his subordinates and to take action within the scope of his position. Authority flows from top to bottom. Authority determines the superior subordinate relationship in an organisation.
2) Responsibility: Responsibility is the obligation of a subordinate to properly perform the assigned duty. Responsibility flows upwards, i.e., a subordinate will always be responsible to his superior.
3) Accountability : Accountability implies being answerable for the final outcome, i.e., subordinate will be accountable to a superior for satisfactory performance of work.
Question 9.
‘Clever Dogs’ is a leading IT Company in Techno Park at Thiruvananthapuram and the organisation has its necessary hierarchical position. The employees of this firm decided to form a Carol Club for its X-mas celebrations and Mr. Mathew is elected as the convenor. (MARCH-2016)
a) Identify the 2 forms of organisation here.
b) Distinguish between them.
Answer:
a) Ciever Dogs is a formal organisation and Carol Club is an informal organisation, b) Distinction between Formal and Informal organisation.

Question 10.
Briefly describe any five advantages of effective delegation in the case of a business enterprise.(MAY-2016)
Answer:
Importance of Delegation of Authority
1) Reduces the work load of managers : The managers are able to function more efficiently as they get more time to concentrate on important matters.
2) Employee development: Delegation empowers the employees by providing them the chance to use their skills,’gain experience and develop themselves for higher positions.
3) Motivation of employees : Responsibility for work builds the self-esteem of an employee and improves his confidence. He feels encouraged and tries to improvers performance.
4) Facilitation of.growth : Delegation helps in the expansion of an organisation by providing a ready workforce to take up leading positions in new ventures.
5) Superior-subordinate relations: Delegation of authority establishes superior subordinate relationships, which are the basis of hierarchy of management.
6) Better co-ordination: The elements of delegation – authority, responsibility and accountability help to avoid overlapping of duties and duplication of effort.
Question 11.
V-Guard Ltd. a leading company in Kerala is engaged in diversified business namely electricals, textiles, amusement parks etc. Each of this have different departments namely Marketing, Production Finance Research and Development etc. Suggest a suitable organizational structure to this company and list its merits and demerits. (MARCH-2017)
Answer:
Divisional Organisation Structure
b) Advantages
1) Each division functions as an autonomous unit which leads to faster decision making.
2) It helps in fixation of responsibility in cases of poor performance of the division
c) Disadvantages
1) Conflict may arise among different divisions with reference to allocation of funds.
2) ft may lead to increase in costs since there may be a duplication of activities across products.
Question 12.
It is often accepted that, instead of having a confronting attitude, management should skill fully take the advantages of both formal and informal organisation. Substantiate. (MAY-2017)
Answer:
Advantages
1) It is easier to fix responsibility since mutual relationships are clearly defined.
2) Clear determination of duties, authorities and responsibilities. It helps in avoiding duplication of effort.
3) Unity of command is maintained through an established chain of command.
4) It provides stability to the organisation.
5) Co-ordination and control become easy.
Advantages
1) There can be faster spread of communication.
2) It helps to fulfil the social needs of the members and this enhances their jpb satisfaction.
3) Top level managers can know the real feedback of employees on various policies and plans.
Plus Two Business Studies Organising 8 Marks Important Questions
Question 1.
Explain the concept of delegation and decentralisation bringing out their distinction.(FEBRUARY – 2009)
Answer:
Organising is one of the most important functions of management, which includes
1) Identifying and grouping the work to be performed.
2) Defining and delegating authority and responsibility.
3) and establising relationships for the purpose of accomplishing objectives
Question 2.
Joy Ltd. is having an organisational structure which is intentionally created with well defined jobs. (MARCH-2009)
a) Identifythe type of organisation, miniojm
b) State its features.
c) Locate its difference from an organisation created on personal and social relationship on the basis of friendship.
Answer:
a) Formal Organisation
b) Features
1) It is deliberately created by the top management to achieve the objectives.
2) It is based on division of labour and specialisation.
3) It is impersonal – Does not take into consideration emotional aspect of employees.
4) It clearly defines the authority and responsibility of every individual.
5) The principle of scalar chain is followed in formal organisation.
c)

Question 3.
Salma Ltd., a firm manufacturing shampoo has the following departments. Purchase, Marketing, Produc-tion, Finance and Human Resources Department. (MARCH-2009)
Mr. Basheer, the general manage,r was taking all major decisions of the different departments. The company decided to introduce herbal shampoo in the market. In the circumstances of work overload, Mr. Basheer decided to grant some authority to his subordinates.
a) What is the concept referred to?
b) State the importance of this concept
c) How does it differ from decentralisation?
Answer:
a) Delegation of authority
b) Importance of Delegation of Authority
1) Reduces the work load of managers : The managers are able to function more efficiently as they get more time to concentrate on important matters.
2) Employee development: Delegation empowers the employees by providing them the chance to use their skills,’gain experience and develop themselves for higher positions.
3) Motivation of employees : Responsibility for work builds the self-esteem of an employee and improves his confidence. He feels encouraged and tries to improvers performance.
4) Facilitation of.growth : Delegation helps in the expansion of an organisation by providing a ready workforce to take up leading positions in new ventures.
5) Superior-subordinate relations: Delegation of authority establishes superior subordinate relationships, which are the basis of hierarchy of management.
6) Better co-ordination: The elements of delegation – authority, responsibility and accountability help to avoid overlapping of duties and duplication of effort.
c)