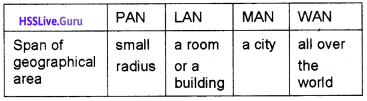
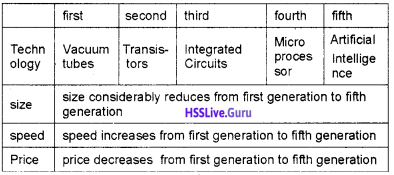
Students can Download Chapter 3 Components of the Computer System Questions and Answers, Plus One Computer Science Chapter Wise Questions and Answers helps you to revise the complete Kerala State Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Kerala Plus One Computer Science Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 3 Components of the Computer System
Plus One Components of the Computer System One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The Tangible parts of a computer is _________
Answer:
Hardware

Question 2.
The instructions that tell the hardware to perform a task is __________
Answer:
Software
Question 3.
The brain of the computer is __________
Answer:
CPU
Question 4.
CPU means _________
Answer:
Central Processing Unit
Question 5.
ALU is
Answer:
Arithmetic Logic Unit
Question 6.
I am an input device. I can read text or picture on paper and translate into computer usable form. Who am I?
Answer:
Scanner
Question 7.
Odd man out.
(a) Trackball
(b) Joy Stick
(c) Scanner
(d) LCD
Answer:
(d) LCD. It is an output device. Others are input device
Question 8.
Odd man out.
(a) Inkjet
(b) Laser
(c) Dot Matrix Printer
(d) Thermal
Answer:
(c) Dot Matrix Printer. It is impact printer others are non impact printers.

Question 9.
The storage capacity of a CD is ________
(a) 1.44 MB
(b) 700 GB
(c) 700 MB
(d) 650 GB
Answer:
(c) 700 MB
Question 10.
__________ sheet is used to write answers in Kerala Entrance Exam.
Answer:
OMR Sheet
Question 11.
ABC textile uses reader to input the item and its price.
Answer:
Bar code reader
Question 12.
_________ device senses the presence or absence of a pencil mark.
Answer:
OMR
Question 13.
Name any two printing devices.
Answer:
Mouse and touchpad
Question 14.
__________ is a device that draws pictures on a paper.
Answer:
Plotter
Question 15.
Primary memory is classified into two. What are they?
Answer:
RAM and ROM
Question 16.
The storage capacity of a DVD is _________.
Answer:
4.7 GB
Question 17.
Winzip is a ___________ utility.
Answer:
Compression utility
Question 18.
Win Rar is a ________ utility.
Answer:
Compression utility
Question 19.
Most commonly used input device is _________________
Answer:
Keyboard or mouse
Question 20.
Govt, decided to conduct a test that contains all objective type questions. Which device is most suitable for evaluation.
Answer:
OMR
Question 21.
__________ is used mostly for computer games.
Answer:
Joy stick
Question 22.
I am an input device. I have a stick with two buttons called triggers on the top. Who am I?
Answer:
Joy stick
Question 23.
I am a pointing device. I am a stationary device. Who am I?
Answer:
Touchpad
Question 24.
In portable computers which pointing device is suitable?
Answer:
Touchpad
Question 25.
State true or false.
Hard copy devices are very slow compared to soft copy devices.
Answer:
True

Question 26.
________ is also called firrfi ware.
Answer:
ROM
Question 27.
__________ is acts as an interface between user and computer.
Answer:
Operating system
Question 28.
_________ is used to create and modify any type of document.
Answer:
Word Processor
Question 29.
_________ is a set of programs that manage the database.
Answer:
DBMS
Question 30.
__________ package contains rows & columns.
Answer:
Spread sheet
Question 31.
_________ is a presentation package.
Answer:
Power point
Question 32.
Your computer teacher asked you to explain the project work done by your group. Which package will help you to do so?
Answer:
Power Point
Question 33.
___________ is a DTP Package.
(a) Excel
(b) Powerpoint
(c) PageMaker
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) PageMaker
Question 34.
DTP is ________
Answer:
Desk Top Publishing
Question 35.
_______ is designed to help computer for its smooth functioning.
Answer:
Utilities
Question 36.
Customised software is also called _________
Answer:
Tailor made software
Question 37.
__________ S/W is used to remove virus from a computer.
Answer:
Anti Virus S/W
Question 38.
Name any Antivirus S/W.
Answer:
Norton Antivirus, McAfee, Avira, AVG
Question 39.
Name the two classifications of output devices.
Answer:
Hard copy and soft copy
Question 40.
Name the two classifications of printers.
Answer:
Impact printer and non-impact printer
Question 41.
_______ gas is used in plasma panels
Answer:
(a) Oxygen
(b) Neon
(c) Mercury
(d) helium Neon
Answer:
(b) Neon
Question 42.
__________ printers are used in fax machine.
Answer:
Thermal Printers
Question 43.
_________ is read/write memory.
Answer:
RAM
Question 44.
________ is of volatile memory
(a) ROM
(b) RAM
(c) CD
(d) DVD
Answer:
(b) RAM

Question 45.
From the following which is expensive?
(a) CD
(b) DVD
(c) HDD
(d) RAM
Answer:
(d) RAM
Question 46.
You want to input your photograph into computer. Which device is used for this?
(a) Scanner
(b) Mouse
(c) OMR
(d) OCR
Answer:
(a) Scanner
Question 47.
The primary memory which is commonly used in electronic billing machines to store price of products is
(a) P R O M
(b) E P R O M
(c) E E P R O M
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) E P R O M
Question 48.
Name any three pointing devices,
Answer:
Mouse, Touchpad and light pen.
Question 49.
You want to print your brother’s resume which printer will you choose. Why?
Answer:
I will choose either Ink-jet or Laser printer. Because these produce less noise and produce high quality printing output. They are used to print characters as well as graphics (Photos) with very high quality.
Question 50.
The fastest memory in a computer is
Answer:
Registers
Question 51.
The storage capacity of a single layer DVD is _______
Answer:
4.7 GB
Question 52.
Give two examples for OS.
Answer:
Windows 7, Windows Vista
Question 53.
A program in execution is called _______
Answer:
Process
Question 54.
Name the software that translates assembly language program into machine language program.
Answer:
Assembler
Question 55.
DBMS stands for _________.
Answer:
Data Base Management System .
Question 56.
Duplicating disc information is called __________.
Answer:
Backup
Question 57.
An example of free and open source software is _______?
Answer:
Linux
Question 58.
The software that gives users a chance to try it before buying is __________
Answer:
Shareware

Question 59.
An example of proprietary software is _________.
Answer:
Tally
Question 60.
Which software is used for calculation?
(a) Word processor
(b) Spreadsheet
(c) Presentation
(d) Multimedia
Answer:
(b) Spreadsheet
Question 61.
Accumulator stores ________
(a) address of data
(b) instruction to be executed
(c) address of next instruction to be executed
(d) intermediate result
Answer:
(d) intermediate result
Question 62.
If Tracks and Sectors : Hard disk, then
___________ : Compact disk
Answer:
Pits and Lands (OR) 0 and 1
Question 63.
Which one of the following file extensions is different from others?
(a) WAV
(b) MP3
(c) PNG
(d) MIDI
Answer:
(c) PNG, the others are audio files.
Question 64.
Which register holds the memory address of next instruction to the executed?
(a) Accumulator
(b) PC
(c) MBR
(d) MAR
Answer:
(b) PC
Question 65.
1. Write the following memory devices in the order of their speed. (fastest to slowest order)
- Cache
- RAM
- Hard Disk
- Registers
2. What do you mean by Freeware and Shareware?
Answer:
1. Memory devices in the order of their speed.
- Registers
- Cache
- RAM
- Hard Disk
2. Freeware and Shareware:
- Freeware: A s/w with Copy right is available free of cost for unlimited use.
- Shareware: It is an introductory pack distributed on a trial basis with limited functionality and period.
Plus One Components of the Computer System Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The Higher Secondary Department wishes to conduct an examination for +1 students with multiple choice questions and publish results as soon as possible. Suggest a method to evaluate the answer scripts and publish the results quickly & correctly with the help of computers.
Answer:
OMR has to be used, it senses the presence or absence of a mark (bubbles) using a high density beam then converted into electric signals for computer. It needs good quality expensive paper and accurate alignment of printing on forms.

Question 2.
Remesh is a graphic designer who prepares his drawing using a computer. He desires for an alternative device by which he can draw directly on the screen. Suggest a device for this and explain it working.
Answer:
Light pens are used for this. It consists fo a photocell placed in a small tube, it is able to detect the light coming from the screen. Hence locate the exact position on the screen. It is used by graphic designers, illustrators and drafting engineers, with the help of CAD to draw directly on the screen.
Question 3.
You might have noticed that in some shops billing is done using computers without typing the item name, price, quantity, etc. Mention the device used for entering data and explain its working.
Answer:
A device called Bar Code Reader is used for this. It contains photoelectric scanner that read the bar code and input the information to the computer attached to it. It helps to reduce the errors and process the bills quickly.
Question 4.
Your scholl has arranged an excursion. You are having an ordinary camera whereas your friend has a digital camera. List the benefits your friend enjoys by using digital camera.
Answer:
- Digital camera does not need film.
- More number of shots can take
- Operational cost is less
- Very easy to manipulate images in digital form using computers.
Question 5.
A medical shop in your locality wishes to purchase a printer for their billing purpose. Which type of printer will you recommend if carbon copies are to be taken. Justify.
Answer:
Dot Matrix Printer. To take carbon copies impact printer is a must, operational cost is less and it can print bills in a moderate speed.
Question 6.
Find the extact match.

Answer:
- D
- C
- B
- A
Question 7.
Your friend wishes to start a DTP centre with facilities to design posters and notices, to scan pictures and modify them and to print them. What would be your suggestions regarding the computer and peripherals?
Answer:
The requriements are computer, scanner, printer and software.
Question 8.
Find the most appropriate match.

Answer:
1 – D
2 – C
3 – A
4 – B
Question 9.
Suggest a suitable device for the following.
- High quality printing
- High quality drawing
- Printing with carbon copies
- Economical printing of small quantities of data
Answer:
- Non impact – Laser printers, Inkjet
- Plotter
- Impact (DMP(Dot Matrix Printer))
- Dot Matrix Printers
Question 10.
“Not all primary memory is volatile”. Justify this statement.
Answer:
Primary Memory (Main memory) is classified into two RAM and ROM. Out of this RAM is volatile but ROM is non-volatile.
Question 11.
Categorise the softwares in the list according to the appropriate classifications given below.
- Classification: OS, Compiler, DTP Software, Compression software, Word processor
- List: Open Office Writer, Photoshop, 7 Zip, MS Word, Unix, C++, PageMaker, Winzip, C, Windows 98.
Answer:
- OS – Unix, Windows 98
- Compiler – C, C++
- DTP Software – Photoshop, PageMaker
- Compression – 7 Zip, Winzip
- Word Processor – Open Office Writer, MS word
Question 12.
Your friend has just assembled a computer. Now he is provided with installation CD’s of MS Word and Microsoft Windows XP. In what order will he install them? Justify your answer.
Answer:
First he has to install the Microsoft Windows XP because it is the OS, it makes the computer to work other programmes. After that only he can install MS Word It is a package.
Question 13.
A group of 20 students is given a test in 6 subjects. The examiner wishes to prepare a neatly formatted mark list with total and Rank. Suggest a suitable software to serve this purpose. Give reasons.
Answer:
The spreadsheet Excel is a suitable software to serve this purpose. It consists of inbuilt functions, that facilitates to find total and rank easily.

Question 14.
A program is written in BASIC, C and assembly language. Mention the difference in converting these programs to machine language.
Answer:
- C – Compiler
- BASIC – Interpreter
- Assembly Language – Assembler
Question 15.
Your friend told you that he has a system. What is a system? Explain.
Answer:
A computer is also called a system. A computer is not a single unit. It consists of more than one unit such as input unit, output unit, memory unit, ALU and control unit. Therefore a computer is called a system.
Question 16.
What is cache memory?
Answer:
A cache (pronounced cash) memory is a high-speed memory placed in between the processor and primary memory to reduce the speed mismatch between these two.
Question 17.
What is the use of program counter register?
Answer:
This register stores the memory address of the next instruction to be executed by the CPU.
Question 18.
What is HDMI?
Answer:
Its full form is High Definition Multimedia Interface. Through this port we can connect high definition quality video and multi channel audio over a single cable.
Question 19.
Give two examples for customized software.
Answer:
- Payroll System: It keeps track of details of employee and their salary details in an organisation
- Inventory Management System: It keeps tack of all about inventory in a company
Question 20.
What do you mean by free and open source s/w?
Answer;
Here “free” means there is no copy right or licensing. That is we can take copies of the s/w or modify the source code without legal permission of its vendor (creator) we can use and distribute its copy to our friends without permission. That is Freedom to use, to modify and redistribute
Question 21.
- What do you mean by cache memory? (1)
- Write the names of the figures given below.

Answer:
1. It is a high speed memory placed in between the CPU and RAM. CPU is a high speed memory compared to RAM. There is a speed mismatch between the CPU and RAM to resolve this problem a high speed memory called cache memory is placed in between the CPU and RAM
2. QR code and Bar Code

Question 22.
What is the role of students in e-Waste disposal?
Answer:
Student’s role in e-Waste disposal
- Stop buying unnecessary electronic equipments
- Repair Faulty electronic equipments instead of buying a new one.
- Give electronic equipments to recycle
- Buy durable, efficient, quality, toxic free, good warranty products
- check the website or call the dealer if there is any exchange scheme
- Buy rechargeable battery products
Plus One Components of the Computer System Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Why is the paper coming from the laser printer hot? Explain.
Answer:
Laser printer uses photocopying technology. It uses a positively charged drum and negatively charged toner (dry powder). A laser beam is used to scan the page to be printed on the drum with positive charge and then rolled through a reservoir of negatively charged toner.
It uses a combination of heat and pressure to adhere the dry powder to the paper. That is why, the paper coming from the laser printer is hot.
Question 2.
Explain the process how data from the hard disk is taken to the processor for processing.
Answer:
A processor is a high speed device. It can access data only from the Primary Memory (RAM). So we have to transfer data from hard disk to RAM. We know that a hard disk is a slow device also. So data is first transferred to RAM.
A RAM is comparatively slower than processor. To reduce the speed mismatch between the RAM and processor, the data has to transfer to CPU registers. Then the processor takes the data from the CPU register because CPU register has almost equal speed as processor.
Question 3.
Why computer is called as a system? (3)
Answer:
A computer is also called a system. A computer is not a single unit. It consists of more than one unit such as input unit, output unit, memory unit, ALU and control unit. Therefore a computer is called a system.
Question 4.
Differentiate hardware and software. (3)
Answer:
The tangible parts of a computer is called hard¬ware. We can see, touch and feel the hardware in a computer. The set of instructions that tell the hardware how to perform a task is called software. Without software computer cannot do anything.
Question 5.
We all have a brain. Just like this, is the computer has a brain? Explain it?
Answer:
Yes. CPU is the brain of a computer. The CPU comprises three parts ALU, Control Unit and Memory. The control unit control the overall functioning of a system. ALU performs all the arithmetic calculations and takes logical decisions. Memory is used for storage of data for future reference.
Question 6.
Explain the various functions of a control unit.
Answer:
The control unit performs the following functions.
- It controls data flow between input device ALU, memory and output devices.
- Normal execution of a program is line by line. The control unit controls this sequence with the help of ALU and memory.
- It controls the decoding and interpretation of in-structions.
Question 7.
Match the following
| 1. Input device | a. Linux |
| 2. Output device | b. Java |
| 3. Secondary Memory | c. Joystick |
| 4. System S/W | d. Plotter |
| 5. Application S/W | e. PROM |
| 6. Primary Memory | f. HDD |
Answer:
1 – c
2 – d
3 – f
4 – a
5 – b
6 – e
Question 8.
Write down the full form of the following.
- VDU
- OMR
Answer:
- VDU – Visual Display Unit
- OMR – Optical Mark Reader

Question 9.
We know that a scanner is a hardware. What do you think of a virus scanner? Explain.
Answer:
We know that a scanner is a hardware but a virus scanner is not a hardware. It is a program. That is a virus scanner is an antivirus software. That scans your disk (HDD, CD, DVD, Pen Drive) for viruses and removes them (if it can), if any virus is found.
Question 10.
Your friend told you that a compiler is a hardware. Is it true? Justify your answer.
Answer:
It is not true. A compiler is not a hardware but it is a software. A compiler is a collection of programs that translates program written in HLL into machine language.
Question 11.
Anil purchased a product from a supermarket and he found that its wrapper contains light and dark bars. What is the purpose of this ?
Answer:
This light and dark bars are called bar code. It is used to record some details about the product such as item code, name, price etc. A device called Bar Code Reader contains photo electric scanner that read the bar code and input the information to the computer attached to it. It helps to reduce error and process the bills quickly.
Question 12.
What are the disadvantages of OMR? (2)
Answer:
The disadvantages are:
- It needs accurate alignment of printing on forms.
- It needs good quality expensive paper.
Question 13.
Differentiate CRT and LCD (OR) Your friend going to purchase a computer. He asked you which is better, CRT or LCD? What is your opinion?
Answer:
The difference between CRT and LCD is given below:
| CRT | LCD |
| It is heavy and bulky | It is neither heavy nor bulky |
| It consumes more power and emits heat | It consumes less power and does not emit heat |
| It is used in desk top computer | It is used with laptop and desktop |
| It is cheaper | It is expensive. |
So LCD is more better than CRT
Question 14.
While you pressing “A” on the keyboard what is actually stored in the memory?
Answer:
The keyboard is an electro mechanical device that is designed to create electronic codes when a key is pressed and this code is transmitted to the memory through the cable. Here while you pressing “A” on the keyboard, the electronic codes corresponding to the ASCII value 01000001 is transmitting to the memory.
Question 15.
Your family friend started a supermarket. He asked you, which printer is suitable to print bills. Give your suggestion.
Answer:
According to my opinion, dot matrix printer is most suitable. Because they are capable of faster printing as well as it is cheap also. It’s printing quality is not good but cost per copy is very cheap. Dot matrix printer consists of a ribbon cartridge that is cheap and can be changed easily. Here we have to print more copies at a time. So dot matrix is suitable.
Question 16.
Suppose your brother is an engineer. He wants to draw some drawings. Which output device is suitable? Explain.
Answer:
Plotter is suitable for him. A plotter is a device that draws pictures ordiagrams on paper based on commands from a computer. Plotters draw lines using a pen. Pen plotters generally use drum or flat bed paper holders.
In a drum plotter the paper is mounted on the surface of a drum. Here the paper is rotated. But in a flatbed plotter the paper does not move and the pen holding mechanism provides the motion that draws pictures. Plotters are used in engineering applications where precision is needed.
Question 17.
Match the following.
| 1. Operating System | a. Compiler |
| 2. Language Processor | b. Windows Vista |
| 3. Package Administratin S/W | c. Santhi Hospital |
| 4. Utility | d. Spreadsheet |
| 5. Customised S/W | e. Disk defragmenter |
Answer:
1 – b
2 – a
3 – d
4 – e
5 – c

Question 18.
There are special purpose storage locations within the CPU. What are they explain ?
Answer:
Registers are special purpose storage locations within the CPU. They are temporary storage locations. The processing power of a CPU depends on register. Registers appears with storage capacity of 8 bits, 16 bits, 32 bits an 64 bits. They accept, store and transfer data from the CPU at a very high speed.
- Program Counter: This register stores the memory address of the next instruction to be executed by the CPU.
- Instruction Register: The instruction to be executed is stored in this register.
- Memory Address Register: The address on the memory location from which data has to be read is stored here.
- Memory Buffer Register: The data read from the location specified by the MAR is stored in this register.
- General Purpose Registers: These are used to store the result and intermediate results during a processing.
Question 19.
What is an operating system?
Answer:
An operating system acts as an interface between user and computer without an operating system computer is a bare machine. That is without an OS computer cannot do anything. The OS not only makes the system convenient to use but also use hardware in an efficient manner,
eg: Windows XP, Vista, Linux, MS Dos, Windows 7.
Question 20.
We know that a computer only knows low level language and human beings use high level language. So how is it possible to communicate? Explain.
Answer:
The language processors translate the programs written in HLL into machine language which is understood by the computer. The different language processors are given below:
1. Assembler:
This language processor translates programs written in assembly language into machine language.
2. Interpreter:
This language processor translates programs written in HLL into machine language by converting and executing it line by line. If there is any error, the execution is stopped we, can continue after the correction of the program.
3. Compiler:
This language processor is same as interpreter. But it translates HLL into machine language by converting whole lines at a time. If there is any error, correcting all the errors then only it will execute.
Question 21.
Normally a CD contains 700 MB. Is it possible to store a file with size 1 GB? Explain.
OR
Normally a Car has a seating capacity of 5 persons including the driver. But some adjustments more persons can be accommodated in Car. This is connected with a utility. Which is the utility? Explain.
Answer:
Compression utility is used for this. By using compression utility programs we can reduce the file size upto the one third of the file size. So by using this we can reduce 1GB file and store in a CD. It is provided by the OS.
The other compression utility programs are Winzip, WinRar etc. It is possible to compress the files and when needed, these compressed files can be uncompressed and it is restored to their original form.
Question 22.
What is a Virus?
Answer:
A virus is a bad program or harmful program to damage routine working of a computer system. It reduces the speed of a computer. It may be delete the useful system files and make the computer useless.
Question 23.
What do you mean by Utilities?
Answer:
Utilities are useful programs which are designed to help computer for its smooth functioning. Some utilities are back up utility, Disk defragmentation. Virus scanner, etc. It is provided by the O.S.

Question 24.
Differentiate RAM and ROM.
Answer:
The difference between RAM and ROM is given below.
| RAM | ROM |
| 1. It is Random Access Memory | 1. It is Read only Memory |
| 2. It is Read/Write memory | 2. We can’t write but we can only read memory. |
| 3. It is temporary | 3. It is permanently stored. |
| 4. It is volatile | 4. It is non volatile |
| 5. RAM is faster | 5. It is slower |
| 6. It is used to store data and instructions needed by CPU for processing | 6. It contains instructions to check the hardware components, BIOS operations etc. |
| 7. It is also called firmware. |
Question 25.
Mention any two functions of OS.
Answer:
Major functions of an operating System
- Process management: It includes allocation and de allocation of processes(program in execution) as well as scheduling system resources in efficient manner
- Memory management: It takes care of allocation and de allocation of memory in efficient manner
- File management: This includes organizing, naming, storing, retrieving, sharing, protecting and recovery of files.
- Device management: Many devices are connected to a computer so it must be handled efficiently.
Question 26.
Give two examples of human ware.
Answer:
(Write any two from the following). The term refers the persons who use computer System Administrator: It is a person who has central control over the computer systems.
- System Managers: He is responsible for all business transactions with all vendors and contractors.
- System Analysts: He is responsible to improve the productivity and efficiency.
- Database Administrator: It is a person who has a central control over the DBMS.
- Computer Engineer: The person design either h/w or s/w of a computer system.
- Application Programmer: These are computer professionals who interact with the DBMS through programs.
- Computer operators: He is an end user and does not know computer in detail.
Question 27.
Explain how e-waste creates environmental and health problems. What are the different methods for e-waste disposal? Which one is the most effective in your point of view? Why? (5)
Answer:
e-Waste(electronic waste): It refers to the malfunctioning electronic products such as faulty computers, mobile phones, tv sets, toys, CFL, batteries etc. It contains poisonous substances such as lead, mercury, cadmium etc and may cause diseases if not properly managed.
A small amount is recycled. Due to this our natural resources are contaminated(poisoned). Some of them can .recycle properly. But it is a very big problem in front of the Government to collect segregate, recycle and disposal of e-Waste.
e-Waste disposal methods:
- Reuse: Reusability has an important role of e-Waste management and can reduce the volume of e-Waste
- Incineration : It is the process of burning e-Waste at high temperature in a chimney
- Recycling of e-Waste: It is the process of making new products from this e-Waste.
- Landfilling: It is used to level pits and cover by thick layer of soil.

Question 28.
What do you mean by e-waste? Explain the role of students in e-waste disposal.
Answer:
e-Waste(electronic waste): It refers to the malfunctioning electronic products such as faulty computers, mobile phones, tv sets, toys, CFLetc. It contains poisonous substances such as lead, mercury, cadmium etc and may cause diseases if not properly managed.
Student’s role in e-Waste disposal
- Stop buying unnecessary electronic equipments
- Repair Faulty electronic equipments instead of buying a new one.
- Give electronic equipments to recycle
- Buy durable, efficient, quality, toxic free, good warranty products
- check the website or call the dealer if there is any exchange scheme
- Buy rechargeable battery products
Plus One Components of the Computer System Five Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write short notes about input devices.
Answer:
An input device is used to supply data to the computer. They are given below:
1. Key board:
It is the most widely used device to input information in the form of words, numbers etc. There are 101 keys on a standard key board. The keys on the key board are often classified into alpha numeric keys (A to Z, Oto 9), function keys (F1 to F12), special purpose keys (Special characters), cursor movement keys (arrow keys). While pressing a key, the corresponding code’s signal is transmitted to the computer.
2. Mouse:
It is a pointing device, that controls the movement of the cursor, or pointer as a display screen. A mouse has two or three buttons, it is often used in GUI oriented computers. Under the mouse there is a ball, when the mouse moves on a flat surface this ball also moves. This mechanical motion is converted into digi¬tal values that represents x and y values of the mouse movement.
3. Optical Mark Reader (OMR):
This device identifies the presence or absence of a pen or pen¬cil mark. It is used to evaluate objective type exams. In this method special preprinted forms r.e designed with circles can be marked with dark pencil or ink.
A high intensity beam in the OMR converts this into computer usable form and detects the number and location of the pencil marks. By using this we can evaluate easily and reduce the errors.
4. Bar code / Quick Response (QR) code reader:
Light and dark bars are used to record item name, code and price is called Bar Code. This information can be read and input into a computer quickly without errors using Bar Code Readers.
It consists of a photo electric scanner and it is used in super market, jewellery, textiles etc. QR codes are similar to barcodes but it uses two dimensional instead of single dimensional used in Barcode.
5. Joy Stick:
It is a device that lets the user move an object quickly on the screen. It has a liver that moves in all directions and controls the pointer or object. It is used for computer games and CAD / CAM systems.
6. Light Pen:
It is an input device that use a light sensitive detector to select objects directly on a display screen using a pen. Light pen has a photocell placed in a small tube. By using light pen, we can locate the exact position on the screen.
7. Scanner:
It is used to read text or pictures printed on paper and translate the information into computer usable form. It is just like a photostat machine but it gives information to the computer.
8. Digital Camera:
By using digital camera, we can take photographs and store in a computer. Therefore we can reduce the use of film. Hence it is economical.
9. Touchpad:
It is a pointing device found on the portable computers(laptop). Just like a mouse it consists of two buttons below the touch surface to do the operations like left click and right click. By using our fingers we can easily operate.
10. Microphone:
By using this device we can convert voice signals into digital form.
11. Biometric sensor:
It is used to read unique human physical features like fingerprints, retina, iris pattern, facial expressions etc. Most of you give these data to the Government for Aadhaar.
12. Smart card reader:
A plastic card(maybe like your ATM card) stores and transmit data with the help of a reader.
13. Digital Camera :
By using digital camera, we can take photographs and store in a computer. Therefore we can reduce the use of film. Hence it is economical.

Question 2.
Briefly explain the various visual display units.
Answer:
The visual display units are given below:
1. Cathode Ray Tube (CRT):
There are two types of CRT’s, monochrome (Black and white) and colour. Monochrome CRT consists of one elec-tron gun but colour CRT consists of 3 electron guns (Red, Green and Blue) at one end and the other end coated with phosphor. It is a vacuum tube. The phosphor coated screen can glow when electron beams produced by electron guns hit.
It is possible to create all the colours using Red, Green and Blue. The images produced by this is refreshed at the rate of 50 or 60 times each second.Its disadvantage is it is heavy and bulky. It consumes more power and emits heat. But it is cheap. Nowadays its production is stopped by the company.
2. Liquid Crystal Display (LCD):
It consists of two, electrically conducting plates filled with liquid crystal. The front plate has transparent electrodes and the back plate is a mirror. By applying proper electrical signals across the plates, the liquid crystals either transmit or block the light and then reflecting it back from the mirror to the viewer and hence produce images. It is used in where small sized displays are required.
3. Light Emitting Diocte(LED):
It uses LED behind the liquid crystals in order to light up the screen. It gives a better quality and clear image with wider viewing angle. Its power consumption is less.
4. Plasma Panels:
It consists of two glass plates filled with neon gas. Each plate has several parallel electrodes, right angles to each other. When low voltage is applied between two electrodes, one on each plate, a small portion of gas is glow and hence produce images. Plasma displays provide high resolution but are expensive. It is used in, where quality and size is a matter of concern.
5. Organic Light Emitting Diode(OLED) Monitors:
It is made up of millions of tiny LEDs. OLED monitors are thinner and lighter than LCDs and LEDs. It consumes less power and produce better quality images but it is very expensive.
Question 3.
Your friend wants to buy a printer. He wants to know more about printers. Explain different types of printers.
Answer:
Printer: There are two types of printers impact and non-impact printers. Printers are used to produce hard copy.
Impact Printers: There is a mechanical contact between print head and the paper.
1. Dot Matrix Printer:
Here characters are formed by using dots. The printing head contains a vertical array of pins. The letters are formed by using 5 dot rows and 7 dot columns. Such a pattern is called 5 × 7 matrix.
This head moves across the paper, the selected pins fire against an inked ribbon to form characters by dot. They are capable of faster printing, but their quality is not good.
2. Non-impact Printers:
There is no mechanical contact between print head and paper so carbon copies cannot be possible to take. They are inkjet, laser, thermal printers etc.
(a) Inkjet Printer:
It works in the same fashion as dot matrix printers, but the dots are formed with tiny droplets of ink to be fired from a bottle through a nozzle. These droplets are deflected by an electric field using horizontal and vertical deflection plates to form characters and images.
It is possible to generate colour output. They produce less noise and produce high quality printing output. The printing cost is higher. Here liquid ink is used.
(b) Laser Printer:
It uses photo copying technology. Here instead of liquid ink dry ink powder called toner is used. A drum coated with positively charged photo conductive material is scanned by a laser beam. The positive charges that are illuminated by the beam are dissipated. The drum is then rolled through a reservoir of negatively charged toner which is picked up by the charged portions of the drum.
It adheres to the positive charges and hence creating a page image on the drum. Monochrome laser printer uses a single toner whereas the colour, laser printer uses four toners. Its print quality is good less noise and printing cost is higher.
(c) Thermal Printers:
It is same as dot matrix printer but it needs heat sensitive paper. It produces images by pushing electrically heated pins to the special paper. It does not make an impact on the paper so we cannot produce carbon copies. It produce less noise, low quality print and inexpensive. It is used in fax machine.
3. Plotter:
A plotter is a device that draws pictures ordiagrams on paper based on commands from a computer. Plotters draw lines using a pen. Pen plotters generally use drum or flat bed paper holders. In a drum plotter the paper is mounted on the surface of a drum.
Here the paper is rotated. But in a flatbed plotter the paper does not move and the pen holding mechanism provides the motion that draws pictures. Plotters are used in engineering applications where precision is needed.
4. Three Dimensional (3D) printer: This device is used to print 3D objects.
Question 4.
Your school got two printers. One dot matrix and one Laser printer through ICT scheme of Central Govt. What is the difference between these two printers? Explain.
Answer:
| Laser Printer | Dot Matrix Printer |
| It is non-impact printer | It is impact printer |
| Speed is high | Speed is less |
| Good quality text and | Low quality text and very |
| picture | poor quality picture |
| Less noise | More noise |
| Printing cost is high | Printing cost is low |
| Not possible to take | Possible to take carbon |
| carbon copy | copy |
| Toner is used | Ribbon is used |
Question 5.
Explain Primary Memory in detail.
Answer:
Primary memory is classified into two, Random Access Memory (RAM) and Read Only Memory (ROM). The primary memory holds the data which is to be processed by the CPU and the set of instructions to be executed next. The CPU can access the instructions in the primary memory only.
1. Random Access Memory (RAM):
RAM is used to store data and instructions needed by the CPU for processing. RAM can be used for both reading and writing of data so it is called Read and Write memory. It is a volatile memory, that is contents of the RAM will be lost when the power is turned off.
The invention of integrated circuits (chips) increased the memory capacity and reduced the size and cost. Static RAM, Dynamic RAM, Synchronous Dynamic RAM (SDRAM) are the various types of RAM.
2. Read Only Memory (ROM):
We can read this memory but we cannot write into this memory. It is a nonvolatile memory, that is its contents will not lost when the power is turned off. This memory is stored in the ROM chip at the time of manufacture ing itself hence it is called firmware.
ROM contains instructions to check the hardware components connected to the system, perform some basic input/output operations (BIOS), initiates loading of essential software. The different categories are PROM, EPROM and EE PROM.
(a) PROM (Programmable Read Only Memory):
It is just like WORM. That means the instructions are write once but read many. But we cannot change the instructions.
(b) EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory):
It functions just like PROM. But by using ultraviolet light we can erase the old data and can write new data.
(c) EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory):
Here instead of ultraviolet light electric signals are used to erase old data and write new data under software control. It is highly expensive than regular ROM chips.

Question 6.
Explain secondary memory in detail.
OR
To store large volume of data permanently. Which memory is used? Explain.
Answer:
Primary memory has a limited storage capacity and it is not permanent that is why to store large volume of data permanently secondary memory or storage devices are used. They are of many types and they vary in the capacity of storage, speed of data access and media of storage. Nowadays magnetic disks and optical disks are commonly used.
1. Magnetic Disk:
Magnetic disk allows the storage and retrieval for contents of the disk from anywhere at a moderate speed. Magnetic Disks available in various size and storage capacity but the storage media and data access mechanism are similar.
The storage media is circular platters or disks coated with magnetic material. It consists of a spindle capable of rotating with the help of an electrical motor and a read/write head.
(a) Floppy disk:
Floppy means flexible or soft, it uses flexible disk. Its storage capacity is 1,44MB and slower in data transfer rate.
(b) Hard Disk:
Instead of flexible or soft disk it uses rigid material hence the name hard disk. Its storage capacity and data transfer rate are high and low access time. These are more lasting and less error prone. The accessing mechanism and storage media are combined together in a single unit and connect to the mother board via cable.
Therefore we call it as hard disk drive (HDD). It contains one or more rigid platters coated both sides with a special magnetic material and a spindle. Datas are recorded on either surface of the disk except the outer side of last and first disk. Each surface will have one or more read/write heads (fixed head or movable head).
The spindle is attached to a motor that rotates at high speed typically 7200 rotation per minute (rpm). A floppy disk rotates only at 300 rpm.
2. Optical Disk:
The high power laser uses a concentrated, narrow beam of light, which is focuses and directed with lenses, prisms and mirrors for recording data. The optical disks are given below:
(a) Compact Disk Read Only Memory (CDROM):
The data in CDROM is imprinted.by the manufacturers. The user cannot erase or write on the disk but user can only read its contents. CDROM is written in a single continuous spiral unlike magnetic disks that uses concentric circles. Its storage capacity is 700MB.
(b) Erasable Optical Disk:
The disadvantage of CDROM is that we cannot change or erase the contents. But erasable disks can be changed and erased.
(c) Digital Versatile Disk: It is capable of storing upto 4.7GB and more faster.
(d) Blu-ray Disc:
It is used to read and write High Definition video data as well as to store very huge amount of data. While Cd and DVD uses red laser to read and write but it uses Blue-Violet laser, hence the name Blu ray disc. The blue-violet laser has shorter wavelength than a red laser so it can pack more data tightly.
3. Semiconductor storage (Flash memory): It uses EEPROM chips. It is faster and long lasting.
- USB flash drive: It is also called thumb drive or pen drive. Its capacity varies from 2 GB to 32 GB.
- Flash memory cards: It is used in Camera, Mobile phones, tablets etc to store all types of data.
Question 7.
What do you mean by a computer software? Mention its different classification.
OR
Your friend wants to know more about software. Explain more about different classification.
OR
Your friend told you that COBOL and MS Word are same softwares. Do you agree with him. Explain. What is a software and its classification?
Answer:
A Software is a collection of programs to perform a task. The softwares can be classified into two major groups.
- System software
- Application software

1. System Software:
It is a collection of programs used to manage system resources and control its operations. It is further classified into two.
(a) Operating System
(b) Language Processor
(a) Operating System:
It is collection of programs which acts as an interface between user and computer. Without an operating system computer cannot do anything. Its main function is make the computer usable and use hardware in an efficient manner,
eg: WindowsXP, Windows Vista, Linux, Windows 7, etc.
(b) Language Processes:
We know that a program is a set of instructions. The instructions to the computer are written in different languages. They are high level language (HLL) and low level language. In HLL english like statements are used to write programs. They are C, COBOL, PASCAL, VB, Java etc. HLL is very easy and can be easily understood by the human being.
Low level language are classifed into Assembly Language and Machine Language. In assembly language mnemonics (codes) are used to write programs

In Machine Language 0’s and 1’s are used to write program. It is very difficult but this is the only language which is understood by the computer. Usually programmers prefer HLL to write programs because of its simplicity. But computer understands only machine language. So there is a translation needed. The program which perform this job are language processors.
The different language processors are given below:
1. Assembler:
This converts programs written in assembly language into machine language.
2. Interpreter:
This converts a HLL program into machine language by converting and executing it line by line. The first line is converted if there is no error it will be executed otherwise you have to correct it and the second line and so on.
3. Compiler:
It is same as interpreter but there is a difference, it translate HLL program into machine language by converting all the lines at a time. If there is no error then only it will executed.
2. Application Software:
Programs developed to serve a particular application is known as application software, eg:- MS Office, Compression Utility, Tally etc.
Application software can further be sub divided into three categories.
(a) Packages
(b) Utilities
(c) Customized Software

(a) Packages:
Application software that makes the computer useful for people to do every task. Packages are used to do general purpose application.
They are given below:
1. Word Processes:
This is used for creation and modification of text document. That means a word processor helps the people to create, edit and format a textual data with less effort and maximum efficiency.
By using word processor we can change font and font size of character, change alignment (left, right, center and justify), check spelling and grammar of the whole document etc. eg: MS Word.
2. Spread Sheets:
It contains data or information in rows and columns and can perform calculation (Arithmetic, Relational and logi¬cal operation). It helps to calculate results of a particular formula and the formula can apply different cells (A cell is the intersection of a row and column. Each column carries an alphabet for its name and row is numbered).
It is used to prepare budgets, balance sheets, P & L account, Payroll etc. We can easily prepare graphs and charts using data entered in a worksheet. A file is a workbook that contains one or more worksheets, eg: MS Excel is a spreadsheet software.
3. Presentation and Graphics:
You can present your idea with sound and visual effects with the help of presentation software by preparing slides. The application software that manipulate visual images is known as graphics software. eg: MS Power Point is a presentation package.
4. Data base package:
Database is a collection of large volume of data. DBMS is a set of programs that manages the datas are for the centralised control of data such that creating new records to the database, deleting, records whenever not wanted from the database and modification of the existing database. Example for a DBMS is MS Access.
(b) Utilities: Utilities are programs which are designed to assist computer for its smooth functioning.
The utilities are given below:
1. Text editor:
It is used for creating and editing text files.
2. Backup utility:
Creating a copy of files in another location to protect them against loss, if your hard disk fails or you accidently overwrite or delete data.
3. Compression Utility:
It is used to reduce the size of a file by using a program and can be restored to its original form when needed.
4. Disk Defragmenter:
It is used to speeds up disk access by rearranging the files that are stored in different locations as fragments to contiguous memory and free space is consolidated in one contiguous block.
5. Vims Scanner:
It is a program called antivirus software scans the disk for viruses and removes them if any virus is found.
(c) Customised software:
It is collection of programs which are developed to meet user needs to serve a particular application. It is also called tailor made software.
Question 8.
To use a computer not only the hardware but also software are required. Explain the classification of software.
Answer:
Software: The set of instructions that tell the hardware how to perform a task is called software. Without software computer cannot do anything. Two types System s/w and Application s/w System software.
It is a collection of programs used to manage system resources and control its operations. It is further classified into two.
- Operating System
- Language Processor
1. Operating System: It is collection of programs which acts as an interface between user and computer. Without an operating system computer cannot do anything. Its main function is make the computer usable and use hardware in an efficient manner, eg: Windows XP, Windows Vista, Linux, Windows 7, etc.
Major functions of an operating System:
- Process management: It includes allocation and de allocation of processes(program in execution) as well as scheduling system resources in efficient manner.
- Memory management: It takes care of allocation and de allocation of memory in efficient manner
- File management: This includes organizing, naming , storing, retrieving, sharing , protecting . and recovery of files.
- Device management: Many devices are connected to a computer so it must be handled efficiently.

2. Language Processes:
We know that a program is a set of instructions. The instructions to the computer are written in different languages. They are high level language (HLL) and low level language. In HLL English like statements are used to write programs. They, are C, C++, COBOL, PASCAL, VB, Java etc. HLL is very easy and can be easily understood by the human being.
Low level language are classified into Assembly Language and Machine Language.
In assembly language mnemonics (codes) are used to write programs

In Machine Language 0’s and 1’s are used to write program. It is very difficult but this is the only language which is understood by the computer. Usually programmers prefer HLL to write programs because of its simplicity. But computer understands only machine language. So there is a translation needed. The program which perform this job are language processors.
The different language processors are given below:
1. Assembler:
This converts programs written in assembly language into machine language.
2. Interpreter:
This converts a HLL program into machine language by converting and executing it line by line. The first line is converted if there is no error it will be executed otherwise you have to correct it and the second line and so on.
3. Compiler:
It is same as interpreter but there is a difference it translate HLL program into machine language by converting all the lines at a time. If there is no error then only it will executed.
Application Software:
Programs developed to serve a particular application is known as application software, eg:- MS Office, Compression Utility, Tally etc. Application software can further be sub-divided into three categories.
(a) Packages
(b) Utilities
(c) Customized Software
(a) Packages:
Application software that makes the computer useful for people to do every task. Packages are used to do general purpose application.
They are given below:
1. Word Processes:
This is used for creation and modification of text document. That means a word processor helps the people to create, edit and format a textual data with less effort and maximum efficiency. By using word processor we can change font and font size of character, change alignment (left, right, center and justify), check spelling and grammar of the whole document etc.
eg: MS Word.
2. Spread Sheets:
It contains data or information in rows and columns and can perform calculation (Arithmetic, Relational and logical operation). It helps to calculate results of a particular formula and the formula can apply different cells (A cell is the intersection of a row and column.
Each column carries an alphabet for its name and row is numbered). It is used to prepare budgets, balance sheets, P & L account, Pay roll etc. We can easily prepare graphs and charts using data entered in a worksheet. A file is a work book that contains one or more work sheets,
eg : MS Excel is a spread sheet software.
3. Presentation and Graphics:
You can present your idea with sound and visual effects with the help of presentation software by preparing slides. The application software that manipulate visual images is known as graphics software.
eg: MS Power Point is a presentation package.
4. Data base package:
Data base is a collection of large volume of data. DBMS is a set of programs that manages the datas are for the centralized control of data such that creating new records to the database, deleting, records whenever not wanted from the database and modification of the existing database. Example for a DBMS is MS Access.
DTP Packages: DTP means Desk Top Publishing. By using this we can create books, periodicals, magazines etc. easily and fastly. Now DTP packages are used to create in Malayalam also,
eg: PageMaker.
5. Utilities:
Utilities are programs which are designed to assist computer for its smooth functioning.
The utilities are given below:
- Text editor: It is used for creating and editing text files.
- Backup utility: Creating a copy of files in another location to protect them against loss, if your hard disk fails or you accidentally overwrite or delete data.
- Compression Utility: It is used to reduce the size of a file by using a program and can be restored to its original form when needed.
- Disk Defragmenter: It is used to speeds up disk access by rearranging the files that are stored in different locations as fragments to contiguous memory and free space is consolidated in one contiguous block.
- Virus Scanner: It is a program called antivirus software scans the disk for viruses and removes them if any virus is found.
(c) Specific purpose software (Customized software):
It is collection of programs which are developed to meet user needs to serve a particular application. It is also called tailor made software.

Question 9.
Describe the different types of memories and memory devices in computer with features and examples.
Answer:
Memory:
Storage Unit(Memory Unit): A computer has huge storage capacity. It is used to store data and instructions before starts the processing. Secondly it stores the intermediate results and thirdly it stores information(processed data), that is the final results before send to the output unit(Visual Display Unit, Printer, etc)
Memory measuring units are given below.
- 1 bit = 1 or 0(Binary Digit)
- 4 bits = 1 Nibble
- 8 bits = 1 Byte
- 1024 Bytes = 1 KB(Kilo Byte)
- 1024 KB = 1 MB(MegaByte)
- 1024 MB = 1 GB(Giga Byte)
- 1024 GB = 1 TB(Tera Byte)
- 1024 TB = 1 PB(Peta Byte)
Two Types of storage unit:
1. Primary Storage alias Main Memory:
It is further be classified into Two Random Access Memory (RAM) and Read Only Memory(ROM). The one and only memory that the CPU can directly access is the main memory at a very high speed.
It is expensive hence storage capacity is less. RAM is volatile(when the power is switched off the content will be erased) in nature but ROM is non volatile(lt is permanent). In ROM a “boot up” program called BIOS(Basic Input Output System) is stored to “boots up” the computer when it switched on. Some ROMs are given below.
- PROM(Programmable ROM): It is programmed at the time of manufacturing and cannot be erased.
- EPROM (Erasable PROM): It can be erased and can be reprogrammed using special electronic circuit.
- EEPROM (Electrically EPROM): It can be erased and rewritten electrically
Cache Memory:
The processor is a very high speed memory but comparatively RAM is slower than Processor. So there is a speed mismatch between the RAM and Processor, to resolve this a high speed memory is placed in between these two this memory is called cache memory. Commonly used cache memories are Level(L1) Cache(128 KB), L2(1 MB),L3(8 MB), L4(128MB).
2. Secondary Storage alias Auxiliary Memory :
Because of limited storage capacity of primary memory its need arises. When a user saves a file, it will be stored in this memory hence it is permanent in nature and its capacity is huge. Eg: Hard Disc Drive(HDD), Compact Disc(CD), DVD, Pen Drive, Blu Ray Disc etc.
(a) Magnetic storage device:
It uses plastic tape or metal/plastic discs coated with magnetic material.
Hard Disk: Instead of flexible or soft disk it uses rigid material hence the name hard disk. Its storage capacity and data transfer rate are high and low access time.
These are more lasting and less error prone. The accessing mechanism and storage media are combined together in a single unit and connect to the mother board via cable.
(b) Optical storage device:
Optical Disk: The high power laser uses a concentrated, narrow beam of light, which is focuses and directed with lenses, prisms and mirrors for recording data. This beams burns very very small spots in master disk, which is used for making molds and these molds are used for making copies on plastic disks.
A thin layer of aluminium followed by a transparent plastic layer is deposited on it. The holes made by the laser beam are called pits, interpreted as bit 0 and unburned areas are called lands interpreted as bit 1. Lower power laser beam is used to retrieve the data.
1. DVD(Digital Versatile Disc):
It is similar to CD but its storage capacity is much higher. The capacity of a DVD starts from 4.7 GB
2. Blu-ray Disc:
It is used to read and write High Definition video data as well as to store very huge amount of data. While Cd and DVD uses red laserto read and write but it uses Blue-Violet laser, hence the name Blu ray disc. The blue violet laser has shorter wave length than a red laser so it can pack more data tightly.
3. Semiconductor storage (Flash memory):
It uses EEPROM chips. It is faster and long lasting.
- USB flash drive: It is also called thumb drive or pen drive. Its capacity varfes from 2 GB to 32 GB.
- Flash memory cards: It is used in Camera, Mobile phones, tablets etc to store all types of data.
Question 10.
Explain how e-Waste creates environmental issues. Usually there are four methods for e-Waste dispoal. Which one is the most effective? Why? Write a slogan to aware the public about e-Waste hazards.
Answer:
e-Waste disposal methods:
- Reuse: Reusability has an important role of e-Waste management and can reduce the volume of e-Waste
- Incineration: It is the process of burning e-Waste at high temperature in a chimney
- Recycling of e-Waste: It is the process of making new products from this e-Waste.
- Land filling: It is used to level pits and cover by thick layer of soil.

Question 11.
With the help of a block diagram, explain the functional units of a computer.
Answer:
Functional units of computer:
A computer is not a single unit but it consists of many functional units(intended to perform jobs) such as Input unit, Central Processing Unit(ALU and Control Unit), Storage (Memory) Unit and Output Unit.
1. Input Unit:
Its aim is to supply data (Alphanumeric, image , audio, video, etc.) to the computer for processing. The Input devices are keyboard, mouse, scanner,mic, camera,etc
2. Central Processing Unit (CPU):
It is the brain of the computer and consists of three components
- Arithmetic Logic Unit(ALU): As the name implies it performs all calculations and comparison operations.
- Control Unit(CU): It controls overall functions of a computer
- Registers: It stores the intermediate results temporarily.
3. Storage Unit(Memory Unit):
A computer has huge storage capacity. It is used to store data and instructions before starts the processing. Secondly it stores the intermediate results and thirdly it stores information(processed data), that is the final results before send to the output unit(Visual Display Unit, Printer, etc)
Two Types of storage unit
(a) Primary Storage alias Main Memory:
It is further be classified into Two- Random Access Memory(RAM) and Read Only Memory(ROM). The one and only memory that the CPU can directly access is the main memory at a very high speed.
It is expensive hence storage capacity is less. RAM is volatile (when the power is switched off the content will be erased) in nature but ROM is non volatile(lt is permanent)
(b) Secondary Storage alias Auxiliary Memory:
Because of limited storage capacity of primary memory its need arises. When a user saves a file, it will be stored in this memory hence it is permanent in nature and its capacity is huge. eg: Hard Disc Drive(HDD), Compact Disc(CD), DVD, Pen Drive, Blu Ray Disc etc.
4. Output Unit:
After processing the data we will get information as result, that will be given to the end user through the output unit in a human readable form. Normally monitor and printer are used.
![]()