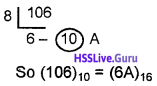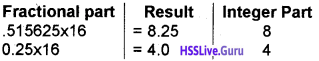Students can Download Chapter 7 Control Statements Questions and Answers, Plus One Computer Science Chapter Wise Questions and Answers helps you to revise the complete Kerala State Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Kerala Plus One Computer Science Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 7 Control Statements
Plus One Control Statements One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
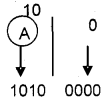
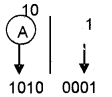
An if statement contains another if statement completely. Then it is known as _________.
Answer:
Nested if
![]()
Question 2.
From the following which is not optional with switch statement.
(a) break
(b) default
(c) case
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) case.
Question 3.
To exit from a switch statement _______ is used.
(a) quit
(b) exit
(c) break
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) break
Question 4.
From the following which statement is true for switch statement.
(a) switch is used to test the equality
(b) switch is used to test relational or logical expression
(c) switch can handle real numbers case data
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) switch is used to test the equality
Question 5.
Sonet wants to execute a statement more than once. From the following which is exactly suitable.
(a) if
(b) loop
(c) switch
(d) if else if ladder
Answer:
(b) loop
Question 6.
Odd one out
(a) for
(b) if
(c) switch
(d) if-else if ladder
Answer:
(a) for. It is a loop the others are branching statement.
Question 7.
Odd one out
(a) for
(b) if
(c) while
(d) do-while
Answer:
(b) if. It is a branching statement and the others are loops.
Question 8.
From the following which loop does the three things, initialisation, checking and updation.
(a) while
(b) do-while
(c) for
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) for
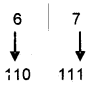
Question 9.
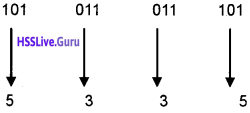
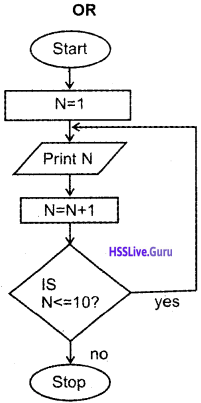
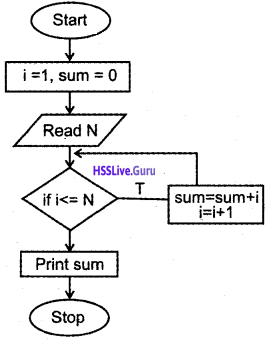
Predict the output Output
(a) 10
(b) 1 to 10
(c) 11
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) 11.
![]()
Question 10.
From the following which is exit controlled loop
(a) for
(b) while
(c) do-while
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) do-while
Question 11.
_____________ statement is used for unconditional jump from one location to another.
Answer:
goto.
Question 12.
Sunitha wants to skip one iteration. From the following which will help her?
(a)continue
(b) break
(c) for
(d) case
Answer:
(a) continue
Question 13.
To terminate a program, from the following which is used.
(a) break
(b) continue
(c) end()
(d) exit()
Answer:
(d) exit()
Question 14.
Which header file is needed to use exit() function in a program?
(a) iostream
(b) cstdlib
(c) math
(d) iomanip
Answer:
(b) cstdlib
Question 15.
In while loop, the loop variable should be updated?
(a) along with while statement
(b) after the while statement
(c) before the while statement
(d) inside the body of while
Answer:
(d) Inside the body of while
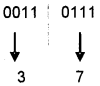
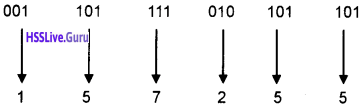
Question 16.
How many times the following loop will execute?
int S = 0, i = 0;
do
{
S + = i;
i++;
} while(i < 5);
Answer:
5 times
![]()
Question 17.
1. statement takes the program control out of the loop even though the test expression is true.
2. Consider the following code fragment. How many times will the character be printed on the screen?
for (i=0; i< 10; i =i+2);
cout <<“*”;
}
Answer:
- break or goto
- Only one time because of semicolon(;) in the end of the for(i=0;i<10;i=i+2);
Question 18.
Which selection statement tests the value of a variable or an expression against a list of integers or character constants? (SAY-2015) (1)
(a) For
(b) If
(c) Switch
(d) Conditional expression
Answer:
(c) switch
Question 19.
How many times the following loop will execute? (MARCH-2016) (1)
int m = 2
do
{
cout<<“Welcome”; m++ ;
} while (m>10);
Answer:
Only one time
Question 20.
________ statement takes the program control outside a loop even though the test expression is true. (SCERT SAMPLE – II) (1)
Answer:
break
Question 21.
Read the following C++ statement for (int n = 1; n<10; n+=2); cout<<n
Now, choose the correct output from the following options. (SCERT SAMPLE – II)(1)
(a) 1
(b) 13579
(c) 11
(d) 10
Answer:
(c) 11. This is because of for statement is end with; (semi colon). Here cout<<n; executes only once.
Question 22.
____________ search method is an example for ‘divide and conquer method’.
Answer:
goto.
![]()
Question 23.
1. Name the type or loop which can be used to ensure that the body of the loop will surely be executed at least once.
2. Consider the code given below and predict the output. (MARCH-2017) (1)
for (int i=1; i<=9;i=i+2)
{
if (i==5) continue;
cout<<i<< ” “;
}
Answer:
- do while loop(Exit controlled loop)
- 1 3 7 9. It bypasses one iteration of the loop when i = 5.
Plus One Control Statements Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Your friend Arun asked you that is there any loop that will do three things, initialization, testing and updation. What is your answer. Explain?
Answer:
Yes. There is only one loop namely for loop that will do this three things. The other loops will do the checking only, initialisation must be do before the loop and updation must be inside the loop.
The syntax of for loop is given below For(initialisation; testing; updation)
{
Body of the for loop;
}
Question 2.
While writing a program Geo uses while loop but forgets to update the loop variable. What will happen?
Answer:
The loop variable inside the while loop must be updated otherwise the loop will not be terminated. The loop will be work infinitely.
Question 3.
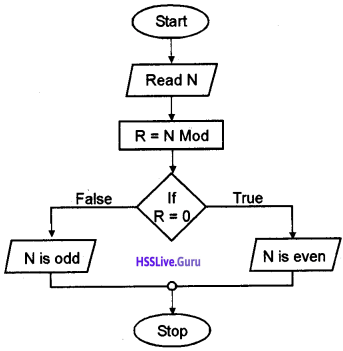
Draw the flow chart of if statement.
Answer:
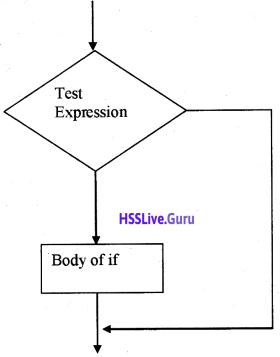
![]()
Question 4.
Draw the flow chart of if else statement
Answer:
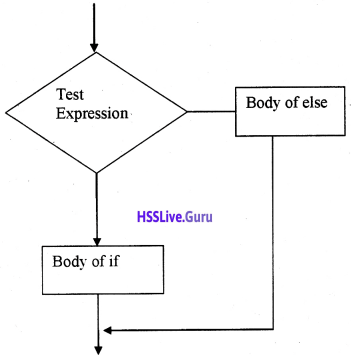
Question 5.
Write a while loop that display numbers from 500 to 550.
Answer:
int i = 500
while (i<=550)
{
cout<<i;
i = i + 1;
}
Question 6.
Distinguish between exit(0) function and return statement
Answer:
Both are used to terminate the program but both are different. Return is a keyword and exit(0) is a function. The difference is, we can use more than one exit(0) function but we can use only one return statement in a scope. To use exit(0), the header file cstdlib should be used.
Question 7.
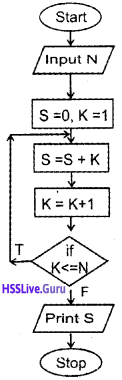
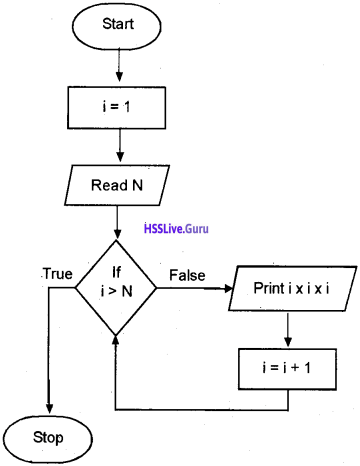
Draw the flowchart of for loop
Answer:
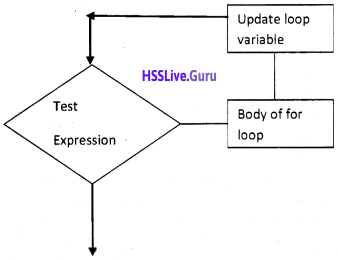
Question 8.
How many time the following for loop will execute? Justify.
for(i = 0; ; i ++)
{
if(i > 5)
cout<<“continue”;
else
cout<<“over”;
}
Answer:
Here the loop becomes infinite because the check condition is missing.
Question 9.
Predict the output.
#include<iostream.h>
int main()
{
int a = 0;
start:
cout<<endl<< ++a;
if(a < 5)
goto start;
}
Answer:
1
2
3
4
3
![]()
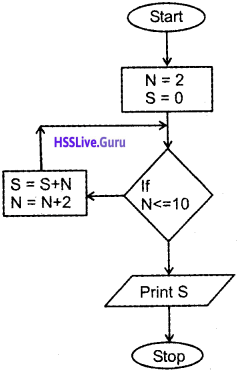
Question 10.
for(int i=2, sum=0; i <= 20; i=i+2)
sum += i;
Rewrite the above code using while loop.
Answer:
int i = 2; sum=0;
while (i<=20)
{
sum += i;
i = i + 2;
}
Question 11,.
Rewrite the following code using switch case statement.
if(day == 1)
cout<<“Sunday”;
else if(day == 2)
cout<<“Monday”;
else if(day == 7)
cout<<“Saturday”;
else
cout <<“Wednesday”;
Answer:
switch (day)
{
case 1: cout<<“Sunday”;break;
case 2: cout<<“Monday”;break;
case 7: cout<<“Saturday”;break;
default : cout<<“Wednesday”;
}
Question 12.
Pick the odd one out from the following. Give reason.
- for, while, do….while
- if, switch, for
Answer:
- do…..while. It is an exit controlled loop while others are entry controlled loop
- for. It is a loop while others are branching statements.
Question 13.
State whether the following statements are True or False. In either case justify your answer.
- Break statement is essential in switch
- For loop is an entry controlled loop
- Do…while loop is an entry controlled loop
- Switch is a selection statement
Answer:
- False. It is not essential in single case statement
- True. Because it will first check the condition. If it is true then only the body will be executed.
- False. It is an exit controlled loop.
- True.
![]()
Question 14.
Write the equivalent code for the following statement. R = (P<Q?P:Q)
Answer:
if(P<Q)
R = P;
else
R = Q;
Question 15.
Examine the following code snippet and find out the output? What will happen if the statement int ch; is replaced by char ch;
int ch;
for(ch=’A’;ch<=’Z’;++ch)
cout<<ch<<”;
Answer:
This code snippet will print 65, 66, 67,……., 90. If the statement int ch; is replaced by char ch; it prints A, B, C, ……., Z.
Question 16.
- _______ is an entry control loop.
- _______ Explain the memory allocation for the following declaration statement. int A[10] [10];
Answer:
- while or for loop
- To store an integer 4 bytes is used in Geany Editor. int A[10] [10]; → It needs 10 × 10 × 4 = 400 bytes
Question 17.
Differentiate between break and continue statements in C++. (SAY -2016) (2)
Answer:
break statement:
It is used to skip over a part of the code i.e. we can premature exit from a loop such as while, do-while, for or switch.
Syntax:
while (expression)
{
if (condition)
break;
}
continue statement:
It bypasses one iteration of the loop. That is it skips one iteration and continue the loop with next iteration value.
Syntax :
while (expression)
{
if (condition)
continue;
}
Plus One Control Statements Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Compare if else and conditional operator?
Answer:
We can use conditional operator as an alternative of if-else statement. The conditional operator is a ternary operator.
The syntax of if-else
if (expression 1)
expression 2;
else
expression 3;
First expression 1 is evaluated if it is true expression 2 will be executed otherwise expression 3 will be executed. Instead of this, we can be written as follows using conditional operator Expression 1 ? expression 2: expression 3;
![]()
Question 2.

Answer:


Question 3.
Rewrite the program following program using if else.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a,b,big;
cout<<“Enter two integers”;
cin>>a>>b;
big = (a>b)?a:b;
cout<<“Biggest number is “<<big<<endl;
return 0;
}
Answer:

![]()
Question 4.


Is it possible to rewrite the above program using switch statement? Distinguish between switch and if else if ladder.
Answer:
No. It is not possible to write the above code using switch statement. Following are the difference between switch and if else if ladder.
- Switch can test only for equality but if can evaluate a relational or logical expression
- If else is more versatile
- If else can handle floating values but switch cannot
- If the test expression contains more variable if-else is used
- Testing a value against a set of constants switch is more efficient than if-else.
Question 5.
Rewrite the following using nested switch construct.

Answer:

![]()
Question 6.
Consider the following output and write down the code for the same.
*
* *
* * *
* * * *
Answer:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i,j;
for(i=1;i<5;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=i;j++)
cout<<n*”;
cout<<endl;
}
}
Question 7.
Consider the following output and write down the code for the same.
1
1 2
1 2 3
1 2 3 4
Answer:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int ij;
for(i=1;i<5;i++)
{
for(j=l;j<=i;j++)
cout<<j<<“”;
cout<<endl;
}
}
Question 8.
Consider the following output and write down the code for the same.
1
2 2
3 3 3
4 4 4 4
Answer:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int ij;
for(i=1;i<5;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=i;j++)
cout<<i<<””;
cout<<endl;
}
}
Question 9.
Consider the following output and write down the code for the same.
1
2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9 10
Answer:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int ij,k=0;
for(i=1;i<5;i++)
{
for(j=l;j<=i;j++)
cout<<++k<<“”;
cout<<endl;
}
}
![]()
Question 10.
Consider the following output and write down the code for the same.
1
1 3
1 3 5
1 3 5 7
Answer:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i,j;
for(i=1;i<5;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=i;j++)
cout<<j × 2-1<<”
cout<<endl;
}
}
Question 11.
Consider the following output and write down the code for the same.
2
4 4
6 6 6
8 8 8 8
Answer:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i,j;
for(i=1;i<5;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=i;j++)
cout<<i × 2<<“”;
cout<<endl;
}
}
Question 12.
Write a program to print the sum of first n natural numbers.
Answer:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n,i,sum=0;
cout<<“Enter a value for n”;
cin>>n;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
sum = sum + i;
}
cout<<“The sum of first ” <<n<<” numbers is “<<sum;
}
Question 13.
Write a program to read a number and check whether it is palindrome or not.
Answer:

![]()
Question 14.
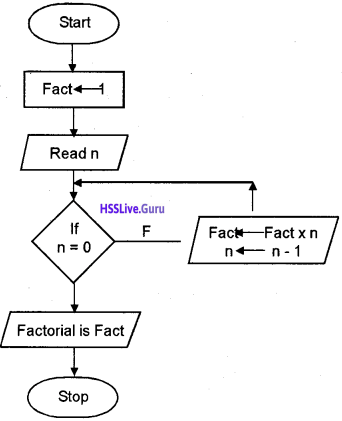
Write a program to print the factorial of a number.
Answer:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n,i;
long fact = 1;
cout<<“Enter a number”;
cin>>n;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
fact = fact × i;
cout<<“The factorial of “<<n<<” is “<<fact;
}
Question 15.
Write a program to print the Fibonacci series.
Answer:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()

Question 16.
Write a program to read a number and check whether the given number is Armstrong or not.
Answer:

Question 17.
Write down the code for the following output using while loop.
*
* *
* * *
* * * *
Answer:

Question 18.
Distinguish between entry controlled loop and exit controlled loop.
Answer:
An entry controlled loop first checks the condition and execute(or enters in to) the body of loop only if it is true. But exit control loop first execute the body of the loop once even if the condition is false then check the condition. The for loop and while loop are entry controlled loops but do-while loop is an exit controlled loop.
![]()
Question 19.
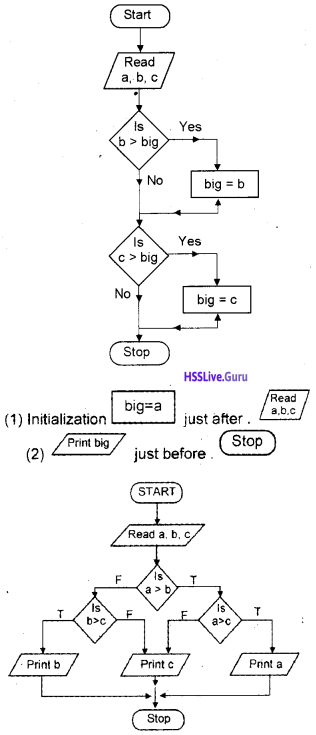
Write a program to find the largest of 3 numbers.
Answer:

Question 20.
Check whether a given number is prime or not.
Answer:

Question 21.
Write a program to print the prime numbers less than 100.
Answer:

Question 22.
Write a program to read number and display its factors.
Answer:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n,i;
cout<<“Enter a number greater than zero”;
cin>>n;
cout<<“The factors are”;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(n%i==0)
cout<<i<<“,”;
}
![]()
Question 23.
Write a program to print the Armstrong numbers less than 1000.
Answer:

Question 24.
Char result;
float marks;
cin>>marks;
if (marks >= 50)
result = ’P’;
else
result = ’F’;
cout<<result;
Rewrite the above code without using if statement.
Answer:
result=(marks>=50) ? ’P’: ’F’;
Question 25.
The output of a program is given below.
1
3
5
7
9
The sum is 25
Write a C++ program for obtaining the above output.
Answer:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int sum=0,i;
for (i=1; i<=9; i+=2)
{
cout<<i<<endl;
sum = sum + i;
}
cout<<“The sum is”<<sum;
}
Question 26.
Find out the error in syntax if any and correct it?
Answer:
1. while (test condition);
{
}
2. do (condition)
{
}while
3. switch (condition)
{
Case 1:
Case 2:
Case 3:
Case 4:
}
Answer:
1. No need of semi colon. The corrected toop is given below
while (test condition)
{
}
2. In do … while loop the while must be end with semicolon.
do (condition)
{
}while;
3. switch contains expression instead of condition switch(expression)
{
Case 1:
Case 2:
Case 3:
Case 4:
}
![]()
Question 27.
Given the total mark of each student in SSLC examination. Write a C++ code fragment to find the grades.
Answer:

Question 28.
You are given the heights of 3 students. Write the relevant code segment to find the maximum height?
Answer:

Question 29.
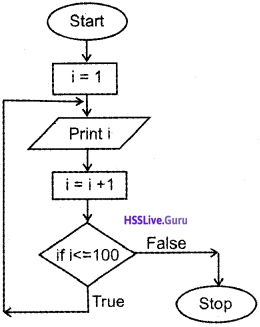
Write the easiest code snippet for printing your name 1000 times. Explain.
Answer:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i;
char name[20];
cout<<“Enter your name:
cin>>name;
for(i=0;i<1000;i++)
cout<<name<<endl;
}
Question 30.
Given a code segment for(i=1; i<10; i++)
cout<<i;
- Rewrite the code using do….while loop
- What will be the output when i = 0? Give reason.
Answer:
1. i = 1;
do{
cout<<i; i++;
}while(i<10);
2. When i = 0, it will execute one more time. ie. the for loop execute 9 times but here this loop executes 10 times.
Question 31.
Whenever a string is entered the inverse of that string is displayed( eg: if we enter ‘CAR’ the output is ‘RAC’). Write a suitable programme for the output.
Answer:

![]()
Question 32.
Write a C++ program to display as follows
A
A B
A B C
A B C D
A B C D E
Answer:

Question 33.
Write C++ program forgetting the following output. (SAY-2016) (3)
1
1 2
1 2 3
1 2 3 4
OR
Consider the following C++ program and answer the following questions.
#include<iostream.h>
int main()
{
int a, p = 1;
for(a=1;a<=5;a+=2)
p = p × a;
cout<<p;
}
(a) Predict the output of the above code.
(b) Rewrite the above program using while loop.
Answer:

Plus One Control Statements Five Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
“We know that the execution of a program is sequential”. Is it possible to change this sequential manner and explain different jump statements in detail.
Answer:
The execution of a program is sequential but we can change this sequential manner by using jump statements. The jump statements are
1. goto statement:
By using goto we can transfer the control anywhere in the program without any condition. The syntax is goto label;
Example:


2. break statement:
It is used to skip over a part of the code i.e. we can premature exit from a loop such as while, do-while, for or switch.

![]()
3. continue statement:
It bypasses one iteration of the loop.


4. exit(0) function:
It is used to terminate the program. For this the header file cstdlib must be included.
Question 2.
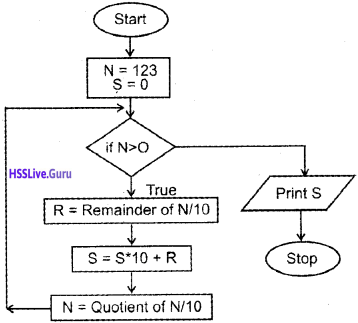
Mr. X wants to get an output 9 when inputting 342 and he also wants to get 12 when inputting 651. Write the program and draw a suitable flowchart for X?
Answer:



Question 3.
Explain conditional statements in detail?
Answer:
1. Simple if:
The syntax is given below if(expression)
statement;
or
if(expression)
{
Block of statements
}
First expression evaluates if it is true then only statement will be executed.
eg: if (n>0)
cout<<n<<” is positive”;
2. if else:
The syntax is given below, if (expression)
statement 1;
else
statement 2;
or
if (expression)
{
statement block 1;
}
else
{
statement block 2;
}
First expression evaluates if it is true statement block 1 will be executed otherwise statement block 2 will be executed. Only one block will be executed at a time so it is called branching statement.
eg:
if (n>0)
cout<<n<<” is positive”;
else
cout<<n<<” is negative”;
3. if else if ladder:
The syntax will be given below
if (expression!)
{
statement block 1;
}
else if (expression 2)
{
statement block 2;
}
else if (expression 3)
{
statement block 3;
}
else
{
statement block n;
}
Here first expression 1 will be evaluated if it is true only the statement blockl will be executed otherwise expression 2 will be executed if it is true only the statement block 2 will be executed and so on. If all the expression evaluated is false then only statement block n will be evaluated .
eg:
If (mark>=90)
cout<<“Your grade is A+”;
else if (mark>=80)
cout<<“Your grade is A”;
else if (mark>=70)
cout<<“Your grade is B+”;
else if (mark>=60)
cout<<“Your grade is B”;
else if (mark>=50)
cout<<”Your grade is C+”;
else if (mark>=40)
cout<<“Your grade is C”;
else if (mark>=30)
cout<<“Your grade is D+”;
else
cout<<“Your grade is D”;
![]()
4. conditional operator:
It is a ternary operator and it is an alternative for if else construct. The syntax is given below.
expression 1? expression 2: expression 3;
or
expression 1? Value if true : value if false;
Here expression 1 will be evaluated if it true expression 2 will be executed otherwise expression 3 will be executed.
eg:
n>0?cout<<n<<” is positive”:cout<<n<<” is negative”;
5. Switch:
It is a multiple branch statement. Its syntax is given below.
switch(expression)
{
case value: statements;break;
case value: statements;break;
case value: statements;break;
case value: statements;break;
case value: statements;break;
……..
default : statements;
}
First expression evaluated and selects the statements with matched case value.
eg:
switch (n)
{
case 1: cout<< “Sunday”;break;
case 2: cout<< “Monday”;break;
case 3: cout<< “Tuesday”;break;
case 4: cout<< “Wedesday”;break;
case 5: cout<< “Thursday”;break;
case 6: cout<< “Friday”;break;
case 7: cout<< “Saturday”;break;
default : cout<< “lnvalid”
}
Question 4.
Explain different loops in detail?
1. For loop:
The syntax of for loop is for(initialization; checking ; update loop variable)
{
Body of loop;
}
First part, initialization is executed once, then checking is carried out if it is true the body of the for loop is executed. Then loop variable is updated and again checking is carried out this process continues until the checking becomes false. It is an entry controlled loop.
eg: for(i=1,j=1;i<=10;i++,j++)
cout<<i<<” × “<<j<<” = “<<i × j;
2. While loop:
It is also an entry controlled loop The syntax is given below
Loop variable initialised while(expression)
{
Body of the loop;
Update loop variable;
}
Here the loop variable must be initialised outside the while loop. Then the expression is evaluated if it is true then only the body of the loop will be executed and the loop variable must be updated inside the body. The body of the loop will be executed until the expression becomes false.
eg:
i = 1;
j = 1;
while(i<=10)
{
cout<<i<<” × “<<j<<” = “<<i × j; i++;
j++;
}
3. do While loop:
It is an exit controlled loop. The syntax is given below
do
{
Statements
}while(expression);
Here the body executes atleast once even if the condition is false. After executing the body it checks the expression if it false it quits the body otherwise the process will be continue.
![]()
Question 5.
Write a program to do the following:
- Inputs the values for variables ‘n’ and ‘m’.
- Prints the numbers between ‘m’ and ‘n’ which are exactly divisible by ‘m’.
- Checks whether the numbers divisible by ‘m’ are odd or even.
OR
Write a program using nested loop that inputs a number ‘n’ which generates an output as follows. Hint: if the value of ‘n’ is 5, the output will be as ‘n’
Answer:
1.
25
25 16
25 16 9
25 16 9 4
25 16 9 4 1
2.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
clrscr();
int i,n,m;
cout<<“Enter values for n and m”;
cin>>n>>m;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(i%m == 0)
cout<<i<<“,”;
getch();
}
3.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
clrscr();
int i,n,m;
cout<<“Enter values for n and m”;
cin>>n>>m;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(i%m == 0)
{
cout<<i<<“\t”;
if(i%2 == 0)
cout<<“even”<<endl;
else
cout<<“odd”<<endl;
}
getch();
}
OR
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<string.h>//for strlen()
main()
{
clrscr();
int n,i,j;
cout<<“enter a value for n:”;
cin>>n;
for(i=n;i>0;i- -)
{
for(j=n;j>=i;j~)
cout<<j × j<<“\t”;
cout<<endl;
}
getch();
}
![]()
Question 6.
Write a C++ program to display Fibonacci series. (SAY-2015)
Answer:


Question 7.
1. Write a C++ program to accept an integer number and check whether it is an Armstrong number or not. (Hint: Sum of the cubes of the digits of an Armstrong number is equal to that number itself)
OR
2. rite a C++ program to accept an integer number and print its reverse (Hint: If 234 is given, the output must be 432).
Answer:
1.

2. #include<iostream>
void main()

Question 8.
1. Write a menu driven program which accepts 3 numbers and show options to find and display.
- the biggest number
- the smallest number
- the sun of the numbers
- the product of the numbers
OR
2. Write a C++ program to check whether a number is palindrome or not.
Answer:
1.


OR
2.

![]()
Question 9.
Answer any one question from 22(a) and 22(b).
1. Write a C++ program to display all leap years between 1000 and 2000 excluding all century years.
OR
2. Write a C++ program to find the sum of the first 10 numbers of Fibonacci series. (Fibonacci series is 0, 1, 1,2, 3, 5, 8, 15 where 0 and 1 are the first two terms and reamaining terms are obtained by the sum of the two preceding terms.)
Answer:
1.

OR
2.

Question 10 (MARCH-2017)
Write a program to check whether the given number is palindrome or not. (MARCH-2017) (5)
OR
Write a program to print the leap years between 2000 and 3000.
(A century year is leap year only if it is divided by 400 and a noncentury year is leap year only if it is divided by 4).
Answer:

OR