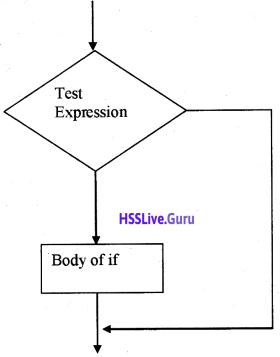
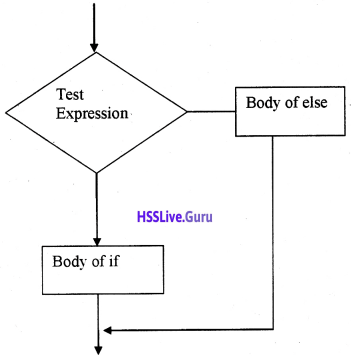
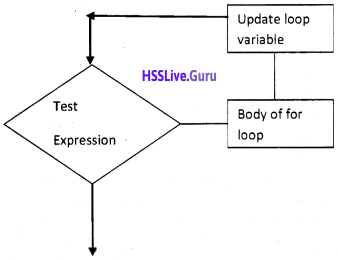
Students can Download Chapter 10 Functions Questions and Answers, Plus One Computer Science Chapter Wise Questions and Answers helps you to revise the complete Kerala State Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Kerala Plus One Computer Science Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 10 Functions
Plus One Functions One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The process of dividing big programs into small programs are called __________.
Answer:
Modularization

Question 2.
The big programs are divided into smaller programs. This smaller programs are called __________.
Answer:
Functions
Question 3.
The execution of the program begins at __________ function.
Answer:
main function
Question 4.
One of the following is not involved in the creation and usage of a user defined function.
(a) Define a function
(b) Declare a function
(c) invoke a function
(d) None of these
Answer:
(d) None of these
Question 5.
The default data type returned by a function is ________.
(a) float
(b) double
(c) int
(d) char
Answer:
(c) int
Question 6.
After the execution of a function, it is returned back to the main function by executing _________ keyword.
Answer:
return
Question 7.
Supplying data to a function from the called func-tion by using _________.
Answer:
parameters (arguments)
Question 8.
_________ keyword is used to give a value back to the called function.
Answer:
return.
Question 9.
_________ key word is used to specify a function returns nothing.
Answer:
void

Question 10.
One of the following is not necessary in the function declaration. What is it?
(a) name of the function
(b) return type
(c) number and type of arguments
(d) name of the parameters
Answer:
(d) name of the parameters
Question 11.
A function declaration is also called _________.
Answer:
prototype
Question 12.
Consider the following declaration
int sum(int a , int b)
{
return a+b;
}
From the following which is the valid function call.
(a) n = sum(10)
(b) n = sum(10,20)
(c) n = sum(10,20,30)
(d) n = sum()
Answer:
(b) n = sum(10,20)
Question 13.
The ability to access a variable or a function from some where in a program is called ________.
Answer:
scope
Question 14.
A variable or a function declared within a function is have ______ scope.
Answer:
local
Question 15.
A variable or a function declared out side of all the functions is have __________ scope.
Answer:
global
Question 16.
State True/False
- A local variable exist till the end of the program
- A global variable destroyed when the sub function terminates
Answer:
- False
- False
Question 17.
consider the following declaration
int x;
void main()
{
……..
}
Here x is a _____ variable.
Answer:
global

Question 18.
consider the following declaration
void main()
{
int x;
}
Here x is a _______ variable
Answer:
local
Question 19.
__________ parameter is used when the function call does not supply a value for parameters
Answer:
default
Question 20.
The parameter used to call a function is called ____________.
Answer:
Actual parameter
Question 21.
The parameters appear in a function definition are ___________.
Answer:
formal parameters
Question 22.
After the distribution of answer scripts, the teacher gives the Photostat copy of the mark list to the students to check the marks. If the students make any change that do not affect the original mark list. There is a similar situation to pass the arguments to a function. What is this method?
(a) call by value
(b) call by reference
(c) call by address
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) call by value
Question 23.
Your class teacher gives you the original mark list to check the mark. If you make any change it will affect the original mark list. There is a similar situation to pass the arguments to a function. What is this method?
(a) call by value
(b) call by reference
(c) call by function
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) call by reference
Question 24.
Consider the following function declaration
int sum(int,a, int b)
{
Body
}
Here the arguments are passed by __________.
Answer:
call by value method

Question 25.
Consider the following function declaration
int sum(int &a, int &b)
{
Body
}
Here the arguments are passed by __________.
Answer:
call by reference method
Question 26.
A function calls it self is known as ____________.
Answer:
recursive function
Question 27.
Varun wants to copy a string by using strcpy() function. From the following which header file is used for this?
(a) cstdio
(b) cmath
(c) cstring
(d) cctype
Answer:
(c) cstring
Question 28.
__________ is a named group of statements to perform a job/task and returns a value.
Answer:
Function
Question 29.
In his C++ program Ajith wants to accept a lengthy text of more than one line. Which function in C++ can be used in this situation.
Answer:
gets() function can be used to accept a lengthy text.
Question 30.
A function can call itself for many times and return a result. What is the name given to such a function? (MARCH-2016)
Answer:
Recursive function
Question 31.
How many values can a C++ function return? (SCERT SAMPLE-I) (1)
Answer:
One Value
Question 32.
A function may require data to perform the task assigned to it. Which is the component of function prototype that serves this purpose? (SCERT SAMPLE – II) (1)
Answer:
Arguments (Parameters)
Question 33.
“Arguments used in call statement are formal arguments”. State true or false. (SAY-2016) (1)
Answer:
False

Question 34.
Name the built-in function to check whether a character is alphanumeric or not. (MARCH-2017)
Answer:
pisalnum()
Plus One Functions Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
How does C++ support modularity in programming C++
Answer:
The process of converting big programs into smaller programs is known as modularisation. This small programs are called modules or sub programs or functions. C++ supports modularity in programming called functions.
Question 2.
Consider the following code snippet
charch;
cout << “Enter an alphabet”;
cin>>ch;
cout<<toupper (ch);
What is the output of the above code? Give a sample output.
If the above code is used in a computer that has no cctype file, how will you modify the code to get the same output?
Answer:
It reads a character and convert it into upper case.
eg:
Enter an alphabet: a
The output is A.
If a computer has no cctype header file the code is as follows,
char ch;
cout<< “Enter an alphabet”;
cin»ch;
if (ch >= 97 && ch<<122)
cout<<ch – 32;
Question 3.
The following assignment statement will generate a compilation error.
char str[20];
str = “Computer”
Write a correct C++ statement to perform the same task
Answer:
char str[20] = “Computer”;
OR
char str[20];
strcpy(str,”Computer”); (The header file <string.h> should be included)
Question 4.
float area(const float pi = 3.1415, const float r)
{
r = 10;
return pi*r;
}
Is there any problem? If yes what is it?
Answer:
There is an error. The error is ‘r’ is a constant V must be initialised and cannot be changed during execution.
Question 5.
Match the following
| a. strcmp() | 1. cctype |
| b. tolower() | 2. iomanip |
| c. sqrt() | 3. iomanip |
| d. abort() | 4. cstdlib |
| e. setw() | 5. cmath |
Answer:
a. 3
b. 1
c. 5
d. 4
e. 2

Question 6.
What are the jobs of a return statement in a program?
Answer:
In the case of a sub function a return statement helps to terminate the sub function and return back to the main function or called function. But in the case of a main function it terminates the program.
Question 7.
How to invoke a function in C++ program?
Answer:
function can be called or invoked by providing the name of the function followed by the arguments in parenthesis.
eg: sum(m,n);
Question 8.
Briefly explain constant arguments
Answer:
By using the keyword const we can make argument (parameter) of a function as a constant argument. The value of the const argument cannot be modified within the function.
Question 9.
Short notes on header files
Answer:
A header file is a prestored file that helps to use some operators and functions. To write C++ pro-grams the header files are must. Following are the header files
alloc
iostream
iomanip
cstdio
cctype
cmath
cstring
The syntax for including a header file is as follows
#include<name of the header file>
eg: #include<iostream>
Question 10.
Identify the appropriate header files for the following.
- setw()
- cout
- toupper()
- exit()
- strcpy()
Answer:
- setw() – iomanip.h
- cout – iostream
- toupper() – cstring
- exit() – process
- strcpy() – cstring
Question 11.
Construct the function prototypes for the following functions.
- The function Display() accepts one argument of type double and does not return any value.
- Total () accepts two arguments of type int, float respectively and returns a float type value. (MARCH-2015) (2)
Answer:
- void Display(double);
- float Total(int, float);

Question 12.
Explain two types of variable according to its scope and life. (SAY-2015) (2)
Answer:
Scope and life of variables and functions
1. Local scope:
A variable declared inside a block can be used only in the block. It cannot be used any other block.
eg:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int sum(int n1 ,int n2)
{
int s;
s = n1 + n2;
return (s);
}
int main()
{
int n1 ,n2;
cout<<“Enter 2 numbers cin>>n1>>n2;
cout<<“The sum is “<<sum(n1 ,n2);
}
Here the variable s is declared inside the function sum and has local scope;
2. Global scope:
A variable declared outside of all blocks can be used any where in the program.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int s;
int sum(int n1,int n2)
{
s = n1 + n2;
return(s);
}
int main()
{
int n1 ,n2;
cout<<“Enter 2 numbers cin>>n1>>n2;
cout<<“The sum is “<<sum(n1,n2);
}
Here the variable s is declared out side of all functions and we can use variable s any where in the program.

Question 13.
There is a way to pass more than one value to the calling function from the called function. Explain how? (SCERT SAMPLE – I) (2)
Answer:
Methods of calling functions
Two types call by value and call by reference.
1. Call by value:
In call by value method the copy of the original value is passed to the function, if the function makes any change will not affect the original value.
Example
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h> void
swap(int a, int b)
{
int temp;
temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
main()
{
clrscr();
int a,b;
cout<<“Enter values for a and b:-“;
cin>>a>>b;
cout<<“The values before swap a =”<<a<<“ and
b =”<<b;
swap(a,b);
cout<<“\nThe values before swap a =”<<a«“ and
b =”<<b;
getch();
}
2. Call by reference:
In call by reference method the address of the original value is passed to the function, if the function makes any change will affect the original value.
Example
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void swap(int &a, int &b)
{
int temp;
temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
main()
{
clrscrO;
int a,b;
cout<<“Enter values for a and b:- “; cin>>a>>b;
cout<<“The values before swap a =”<<a<<“ and
b=”<<b;
swap(a,b);
cout<<“\nThe values before swap a =”<<a<<“ and
b =”<<b;
getch();
}
Question 14.
A
Answer:
int sum (int N, int Start_No) .
{
int i, S = 0;
for (i = Start_No; i < = N + Start_No; i++)
S = S + i;
reurn S;
}
Question 15.
Differentiate between the string functions strcmp() and strcmpi(). (SAY-2016) (2)
Answer:
strcmp(): It is used to compare two strings and returns an integer.
Syntax:
strcmp(string1,string2)
- if it is 0 both strings are equal.
- if it is greater than 0(i.e. +ve) stringl is greater than string2
- if it is less than 0(i.e. -ve) string2 is greater than string1
strcmpi():
It is same as strcmp() but it is not case sensitive. That means uppercase and lowercase are treated as same.
eg: “ANDREA” and “Andrea” and “andrea” these are same.
Question 16.
Read the function definition given below. Predict the output, if the function is called as convert (7). (MARCH-2017) (2)
void convert (int n)
{
if (n>1)
convert (n/2);
cout<<n%2;
}
Answer:
The out put is 111. convert() is a recursive function.
Plus One Functions Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Consider the following function declaration with optional (default) arguments and state legal or illegal and give the reasons
- int sum(int x = 10, int y, int z)
- int sum(int x = 10, int y = 20, int z)
- int sum(int x = 10, int y = 20, int z = 30)
- int sum(int x, int y = 20, int z)
- int sum(int x, int y = 20, int z = 30)
- inf sum(int x, int y, int z = 30)
- int sum(int x = 10, int y, int z = 30)
Answer:
There is a rule to make an argument as default argument,i.e., to set an argument with a value that must be in the order from right to left. All the arguments in the right side of an argument must be set first to make an argument as a default argument.
- illegal, because y and z are not have values
- illegal, because z has no value
- legal
- illegal, because z has no value
- legal
- legal
- illegal, because x has a value but y has no value

Question 2.
A list of C++ built-in functions are given. Classify them based on the usage and prepare a table with proper group names.

Answer:

Question 3.
Read the following program
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout<<sum(2,3);
}
int sum(int x, int y)
{return (x + y);}
On compilation on the program, an error will be displayed. Identify and explain the reason. How can you rectify the problem
Answer:
The compilation of the program starts from the first line arid next line and so on( i.e. line by line). While compiling the line cout<<sum(2,3); The compiler does not understand the word sum(2,3) because it is not declared yet hence the error prototype required. To rectify this problem there are two methods
First method:
Give the function definition just before the main function as follows.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int sum(intx, int y)
{return (x + y);}
int main()
{
cout<<sum(2,3);
}
Second Method:
Give the function declaration(prototype only) in the main function as follows.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int sum(int.int);
cout<<sum(2,3);
}
int sum(int x, int y)
{return (x + y);}
Question 4.
Considering the following function definition.
{
for (int f = 1; n>0; n-)
f = f*n;
return f;
}
void main()
{
int a = 5, ans;
ans = fact (a);
cout<< a << “! = ” << ans;
}
The expected, desired output is 5! = 120
What will be the actual output of the program? It is not the same as above, why? What modification are required in the program to get the desired output.
Answer:
The output is 0! = 120
Because the address of variable ’a’ is given to the variable ‘n’ of the function fact(call by reference method). So the function changes its value (i.e. n-) to 0. Hence the result.
To get the desired result call the function as call by value method in this method the copy of the value of the variable ‘a’ is given to the function. So the actual value of ‘a’ will not changed. So instead of int fact(int &n) just write int fact(int n), i.e., no need of & symbol.

Question 5.
A function is defined as follows
int sum (int a, int b = 2)
{return (a + b);}
Check whether each of the following function calls is correct or wrong, Justify your answer
- cout << sum (2,3);
- cout << sum( 2) ;
- cout << sum();
Answer:
Here the function is declared with one optional argument. So the function call with minimum one argument is compulsory.
- It is valid. Here a becomes 2 and b becomes 3.
- It is also valid . Here a becomes 2 and b takes the default value 2.
- It is not a valid call. One argument is compulsory.
Question 6.
The factorial of a number, say N is the product of first N natural numbers. Thus, factorial of 5 can be obtained by taking the product of 5 and factorial of 4. Similarly factorial of 4 be found out by taking the product of 4 and factorial of 3. At last the factorial of 1 is 1 itself.
Which technique is applicable to find the factorial of a number in this fashion? Write a C++ function to implement this technique. Also explain the working of the function by giving the number 5 as input.
Answer:
A function calls itself is known as recursion.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int fac(int);
int main()
{
int n;
cout<<“enter a number”;
cin>>n;
cout<<fac(n);
}
int fac(int n)
{
if (n == 1) return (1);
else
return (n × fac(n – 1));
}
The working of this program is as follows If the value of n is 5 then it calls the function as fa. The function returns value 5 × fac(4), That means this function calls the function again and returns 5 ×4 × fac(3). This process continues until the value n = 1. So the result is 5 × 4 × 3 × 2 × 1 = 120.
Question 7.
How do two functions exchange data between them? Compare the two methods of data transfer from calling function to called function
Answer:
There are two methods they are call by value and call by reference
1. call by value:
In call by value method, a copy of the actual parameters are passed to the formal parameters. If the function makes any change it will not affect the original value.
2. call by reference:
In call by reference method, the reference of the actual parameters are passed to the formal parameters. If the function makes any change it will affect the original value.
Question 8.
Read the following program
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int a = 0;
int main()
{
int showval(int);
cout<< a; a++;
cout << showval (a);
cout<< a;
}
int showval(int x)
{
int a = 5;
return (a + x);
}
Write down the value displayed by the output of the above program with suitable explanation. What are the inferences drawn regarding the scope of variables?
Answer:
The output is 061.
Global variable: A variable declared out side of all functions it is known as global variable.
Local variable: A variable declared inside of a function it is known as local variable.
If a variable declared inside a function(main or other) with the same name of a global variable. The function uses the value of local variable and does not use the value of the global variable.
Here int a = 0 is a global variable. In the main function the global variable ‘a’ is used. There is no local variable so the value of ‘a’, 0 is displayed. The statement ‘a++’ makes the value of ‘a’ is 1. It calls the function showval with argument ‘a = T.
The argument ‘x’ will get this value i.e. ‘x = 1 But in the function showval there is a local variable ‘a’ its value is 5 is used. So this function returns 6 and it will be displayed. After this the value 1 of the global variable ‘a’ will be displayed. Hence the result 061.

Question 9.
The following are function calling statements. Some of them will be executed, while some other generate compilation error. Write down your opinion on each of them with proper justification Function
- har ch =
- sqrt(25);
- strcat (“Computer”, “Program”);
- double num = pow(2,3,5)
- putchar(getchar());
Answer:
- getch get a character from the console(keyboard) but does not echo to the screen. So we can’t read a character from the console.
- It returns the square root of 25.
- It concatenates Program to computer, i.e. we will get a string “computer program”
- The function pow should contains only two arguments. But here it contains 3 arguments so it is an error. We can write this function as follows Double num = pow(pow(2,3),5)
- It reads a character from the console and display it on the screen.
Question 10.
Write down the operation performed by the following statements.
- int l = strlen(“Computer Program”);
- char ch[ ] = tolower(“My School”);
- cout <<(strcmp(“High”, “Low”)>0 ? toupper(“High”):tolower(“Low”));
Answer:
- The built in function strlen find the length of the string i.e. 16 and assigns it to the variable I.
- This is an error because tolower is a character function.
- This is also an error because tolower and toupper are character functions.
Question 11.
A line of given length with a particular character is to be displayed. For example, ********** js a line with ten asterisks (*). Define a function to achieve this output.
Answer:

Question 12.
Read the following function
int fib(int n)
{
if (n<3)
return 1;
else
return (fib(n – 1) + fib(n – 2));
}
- What is the speciality of this function
- How does it work?
- What will be the output of the following code?
Answer:
- This function is a recursive function. That means the function calls itself.
- It works as follows
- if i = 1, The function fib calls with value 1. i.e. fib(1) returns 1
- if i = 2, The function fib calls with value 2. i.e. fib(2) returns 1
- if i = 3, The function fib calls with value 3. i.e. fib(3) returns fib(2) + fib(1) i.e. it calls the function again.
So the result is 1 + 1 = 2 - if i = 4, The function fib calls with value 4. i.e. fib(4) returns fib(3) + fib(2) i.e. it calls the function again.
So the result is 2 + 1 = 3
- The output will be as follows 1 1 2 3
Question 13.
Explain scope rules of functions and variables in a C++ program
Answer:
Local variable or function:
A variable or function declared inside a function is called local variable or function. This cannot be accessed by the out-side of the function.
eg:
main()
{
int k; // local variable
cout<<sum(a,b); // local function
}
Global variable or function:
A variable or function declared out side of a function is called global variable or function. This can be accessed by any statements.
eg:
int k; // global variable
int sum(int a, int b); // global function
main()
{
}

Question 14.
Briefly explain default arguments Default arguments.
Answer:
A default value can be set for a parameter (argument) of a function. When the user does not give a value the function will take the default value. An important thing remember,is an argument cannot have a default value unless all arguments on its right side must have default value.
Functions with valid default arguments are given below
- float area(int x, int y, int z = 30);
- float area(int x, int y = 20, int z = 30);
- float area(int x = 10, int y = 20, int z = 30);
Functions with invalid default arguments are given below
- float area(int x = 10, int y, int z);
- float area(int x, int y = 20, int z);
- float area(int x = 10, int y = 20, int z);
Question 15.
How to pass an array to function.
Answer:
By using call by reference method we can send an array as argument. We have to send only the array name and its data type. The array name holds the starting address and will access the subsequent elements of an array.
The following example shows this

Question 16.
How to pass a structure to a function.
Answer:
A structure can be passed as argument to a function either call by value or call by reference method. An example is given below to read name and age of a structure and pass it to a function.

Question 17.
Write a program to read a character and check whether it is alphabet or not. If it is an alphabet check whether it is upper case or lower case?
Answer:

Question 18.
Write a program to read 2 strings and join them 2 string.
Answer:

Question 19.
Write a program to read 2 strings and compare it 2 string.
Answer:


Question 20.
Write a program to read a string and display the number of alphabets and digits and special characters.
Answer:

Question 21.
Write a program to perform the following opera-tions on a string
- Length of a string
- Search a character
- Display the string
Answer:



Question 22.
Write short notes about conversion functions.
Answer:
The header file stdlib.h is used for conversion functions.Following are the important conversion functions
1. itoa():
It is used to convert an integer into a string.
eg:
int n = 100;
charstr[20];
itoa(n,str,10);
2. Itoa():
It is used to convert an long into a string.
eg:
long n = 1002345L
char str[20];
ltoa(n,str,10);
3. atoi():
It is used to convert a string into integer
eg:
int n;
str[] = “123”
n = atoi(str);
4. atoll():
It is used to convert a string into long
eg:
long n;
str[] = “123456”
n = atol(str);
Question 23.

- Predict the output of both programs.
- Justify your predictions.
Answer:
1. A. Output
value = 40
B. output
value = 0
2. In the first case (A) the argument x is passed by reference method. So the changes made in the function reflects in main()
In the second case (B) the argument x is passed by value method. So the changes made in the function will not reflect in main()
Question 24.
Consider the following C++ function.
int recfact(int x)
{
if(x == 0)
return 1;
else
return x * recfact(x – 1);
}
- What type of function is this? Explain. (2 Scores)
- What is the output of the above function when x = 5
Answer:
- recursive function. The abilty of a function to call itself is called recursion. A function is said to be recursive if a statement in the body of the function calls itself.
- Output 120

Question 25.
void initialise()
{
int k = 10;
}
int main()
{
int a, b;
float marks;
a = 20;
cout<<“First value =”<< a;
initialise();
b = k + a;
cout<<“New value =”<<b;
}
- Identify the error in the above code and explain its reasons.
- Correct the errors.
Answer:
- K is a local variable in the function initialize 0. It is not accessible in main()
- Making the variable K as global we can correct the error.
Question 26.
Write a program to read 2 strings and join them using string function.
Answer:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char str1 [50],str2[50],str[100];
cout<<“Enter a string:”; gets(strl);
cout<<“Enter another string:”; gets(str2);
strcat(str,str1);
strcat(str,str2);
cout<<“The concatenated string is”<<str;
}

Question 27.
Consider the following code.
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char str1 [] = “123”,str2[] = “45”;
int a,b;
a = atoi(str1);
b = atoi(str2);
cout<<a + b;
}
What will be the output and give the reason?
Answer:
The output is 123 + 45 = 168. Here the conversion function atoi is used to convert the string “123” into integer 123 and “45” into integer 45 so the result.
Question 28.
Name the different methods used for passing arguments to a function. Write the difference between them with examples. (MARCH-2015)
Answer:
Methods of calling functions:
Two types call by value and call by reference.
1. Call by value:
In call by value method the copy of the original value is passed to the function, if the function makes any change will not affect the original value.
Example


2. Call by reference:
In call by reference method the address of the original value is passed to the function, if the function makes any change will affect the original value.
Example

Question 29.
Write a C++ program to display the simple interest using function. (SAY-2015) (3)
Answer:
include < iostream>
using namespace std;
float Simplelnt (float p, int n, float r)
{
return (p*n*r/100);
}
int main()
{
float p, r, SI;
int n;
cout<<“Enter values for p,n,r:”; cin>>p>>n>>r;
SI = Simplelnt (p,n,r); cout<<“simple interest is”<<SI;
}

Question 30.
Write a function’s definition of the above type to find the sum of matural numbers from 1 to N. (Hint: If the value of N is 5, the answer will be 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 = 15). (MARCH – 2016) (3)
Answer:
int sum (int n)
{
if (n == 0)
return 0;
else
return (n + sum (n – 1));
}
Question 31.
A program requires functions for adding 2 numbers, 3 numbers and 4 numbers, How can you provide a solution by writing a single functio0n? (SCERT SAMPLE -1) (3)
Answer:
It can be solved by writing function with default values.
eg: int add (int n1, int n2, int n3 = 0, int n4 = 0)
{
return (n1 + n2 + n3 + n4);
}
This function can be invoked by the following function calling
1. add (5,2);
2. add (5,2,7);
3. add (5,2,7,10);
The 1. Call returns 5 + 2 = 7
2. Call returns 5 + 2 + 7 = 14
3. Call returns 5 + 2 + 7 + 10 = 24
Question 32.
Explain the difference between call-by-value method and call-by-reference method with the help of examples. (SCERT SAMPLE – II) (3)
Answer:
Methods of calling functions:
Two types call by value and call by reference.
1. Call by value:
In call by value method the copy of the original value is passed to the function, if the ’ function makes any change will not affect the original value.
Example


2. Call by reference:
In call by reference method the address of the original value is passed to the function, if the function makes any change will affect the original value.
Example


Question 33.
Explain recursive functions with the help of a suitable example. (SAY-2016) (3)
Answer:
A function calls itself is called recursive function.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void convert(int n)
{
if(n>1)
convert(n/2);
cout<<n % 2;
}
int main()
{
convert(7);
}
Here the function convert is a recursive function, that means it calls itself and output of the above program is 111.
Question 34.
Name the built-in function to check whether a character is alphanumeric or not. (MARCH-2017) (3)
Answer:
isalnum()
Question 35
Briefly explain the three components in the structure of a C++ program. (MARCH-2017) (3)
Answer:
1. Preprocessor directives:
A C++ program starts with the preprocessor directive i.e., # .include, #define, #undef, etc, are such a preprocessor directives. By using #include we can link the header files that are needed to use the functions. By using #define we can define some constants.
eg: #define x 100. Here the value of x becomes 100 and cannot be changed in the program. No semicolon is needed.
2. Header files:
A header file is a pre stored file that helps to use some operators and functions. To write C++ programs the header files are must. Following are the header files iostream
- iomanip
- cstdio
- cctype
- cmath
- cstring
The syntax for including a header file is as follows
#include<name of the header file>
eg: #include<iostream>
3. The main function:
The main function is the first function which is invoked at the time of execution and the program ends within main(). The other functions are invoke from main().
Question 36.
Explain the difference between call by value method and call by reference method with the help of examples. (MARCH-2017) (3)
Answer:
Two types are call by value and call by reference.
1. Call by value:
In call by value method the copy of the original value is passed to the function, if the function makes any change wilt not affect the original value.
Example

2. Call by reference:
In call by reference method the address of the original value is passed to the function, if the function makes any change will affect the original value.
Example


Plus One Functions Five Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Short notes about character functions and string functions
Answer:
A. Character functions:
1. isalnum():
t is used to check whether a character is alphabet or digit. It returns a non zero value if it is an alphabet or digit otherwise it returns zero.
2. isalpha():
It is used to check whether a character is alphabet or not. It returns a non zero value if it is an alphabet otherwise it returns zero.
3. isdigit():
It is used to check whether a character is digit or not. It returns a non zero value if it is digit otherwise it returns zero.
4. islower():
It is used to check whether a character is lower case alphabet or not. It returns a non zero value if it is a lowercase alphabet otherwise it returns zero.
5. isupper():
It is used to check whether a character is upper case alphabet or not. It returns a non zero value if it is an upper case alphabet otherwise it returns zero.
6. tolower():
It is used to convert the alphabet into lower case
7. toupper():
It is used to convert the alphabet into upper case
B. String functions:
1. strcpy():
This function is used to copy one string into another
2. strcat():
This function is used to concatenate(join) second string into first string
3. strlen():
This function is used to find the length of a string.
4. strcmp():
This function is used to compare 2 strings. If the first string is less than second string then it returns a negative value. If the first string is equal to the second string then it returns a value zero and if the first string is greater than the second string then it returns a positive value.

Question 2.
Write functions to perform the following operations
- sqrt()
- power of 2 numbers
- sin
- cos
Answer:


Question 3.
Write a C++ program to display the roots of quadratic equation. (SAY-2015) (5)
Answer:
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>

Question 4.
Explain ‘Call by Value’ and ‘Call by Reference’ methods of function calling with the help of a suitable example. (SAY-2016)
Answer:
Two types are call by value and call by reference.
1. Call by value:
In call by value method the copy of the original value is passed to the function, if the function makes any change will not affect the original value.
Example


2. Call by reference:
In call by reference method the address of the original value is passed to the function, if the function makes any change will affect the original value.
Example


Question 5.
Define network topology. Explain any four network topologies in detail. (SAY-2016)
Answer:
Network topologies:
Physical or logical arrangement of computers on a network is called structure or topology. It is the geometrical arrangement of computers in a network. The major topologies developed are star, bus, ring, tree and mesh
1. Star Topology:
A star topology has a server all other computers are connected to it. If computer A wants to transmit a message to computer B. Then computer A first transmit the message to the server then the server retransmits the message to the computer B.
That means all the messages are transmitted through the server. Advantages are add or remove workstations to a star network is easy and the failure of a workstation will not effect the other. The disadvantage is that if the server fails the entire network will fail.
2. Bus Topology:
Here all the computers are attached to a single cable called bus. Here one computer transmits all other computers listen. Therefore it is called broadcast bus. The transmission from any station will travel in both the direction. The connected computers can hear the message and check whether it is for them or not.
Advantages are add or remove computer is very easy. It requires less cable length and the installation cost is less. Disadvantage is fault detection is very difficult because of no central computer.
3. Ring Topology:
Here all the computers are connected in the shape of a ring and it is a closed loop. Here also there is no central computer. Here a computer transmits a message, which is tagged along with its destination computer’s address. The message travels in one direction and each node check
whether the message is for them. If not, it passes to the next node. FIt requires only short cable length. If a single node fails, at least a portion of the network will fail. To add a node is very difficult.
4. Hybrid Topology:
It is a combination of any two or more network topologies. Tree topology and mesh topology can be considered as hybrid topology.
(a) Tree Topology:
The structure of a tree topology is the shape of an inverted tree with a central node and branches as nodes. It is a variation of bus topology. The data transmission takes place in the way as in bus topology. The disadvantage is that if one node fails, the entire portion will fail.
(b) Mesh Topology:
In this topology each node is connected to more than one node. It is just like a mesh (net). There are multiple paths between computers. If one path fails, we can transmit data through another path.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()



![]()

![]()

![]()
![]()

![]()


![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()

![]()